File Info
| Exam | Cisco Certified Network Associate (200-301 CCNA) |
| Number | 200-301 |
| File Name | Cisco.200-301.ExamCollection.2021-03-03.455q.vcex |
| Size | 18 MB |
| Posted | Mar 03, 2021 |
| Download | Cisco.200-301.ExamCollection.2021-03-03.455q.vcex |
How to open VCEX & EXAM Files?
Files with VCEX & EXAM extensions can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Coupon: MASTEREXAM
With discount: 20%





Demo Questions
Question 1
You are the network administrator for your company and have configured Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) in your network. You recently noticed that when devices send large numbers of CDP neighbor announcements, some devices are crashing. You decide to disable CDP on the router.
Which command should you use to achieve the objective?
- no cdp run
- set cdp disable
- no cdp enable
- no cdp advertise-v2
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
You should use the no cdp run command to disable CDP on the router. Due to a known vulnerability regarding the handling of CDP by Cisco routers and switches when devices send large numbers of CDP neighbor announcements, some devices can crash or cause abnormal system behavior. To overcome this problem, you can disable CDP for the entire router by using the no cdp run command. You cannot use the set cdp disable command to disable CDP on the router. This command disables CDP on an entire Catalyst switch. You cannot use the no cdp enable command to disable CDP on the router. This command disables CDP on a specific interface. You cannot use the no cdp advertise-v2 command to disable CDP on the router. This command disables CDPv2 advertisements. Objective:LAN Switching Fundamentals Sub-Objective:Configure and verify Layer 2 protocols References:Cisco > Support > Using Cisco Discovery Protocol Cisco > Support > Technology Support > Network Management > Cisco's Response to the CDP Issue > Document ID: 13621 You should use the no cdp run command to disable CDP on the router. Due to a known vulnerability regarding the handling of CDP by Cisco routers and switches when devices send large numbers of CDP neighbor announcements, some devices can crash or cause abnormal system behavior. To overcome this problem, you can disable CDP for the entire router by using the no cdp run command.
You cannot use the set cdp disable command to disable CDP on the router. This command disables CDP on an entire Catalyst switch.
You cannot use the no cdp enable command to disable CDP on the router. This command disables CDP on a specific interface.
You cannot use the no cdp advertise-v2 command to disable CDP on the router. This command disables CDPv2 advertisements.
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure and verify Layer 2 protocols
References:
Cisco > Support > Using Cisco Discovery Protocol
Cisco > Support > Technology Support > Network Management > Cisco's Response to the CDP Issue > Document ID: 13621
Question 2
Which is NOT a valid range for private IP addresses?
- 10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255
- 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255
- 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255
- 192.255.255.255-193.0.0.0
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
The range 192.255.255.255 - 193.0.0.0 is a valid public IP address range, not a private IP address range. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) has reserved the following three ranges for private Internet use:10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 (10.0.0.0/8) 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255 (172.16.0.0/12) 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 (192.168.0.0/16) The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) manages and distributes global public IP addresses. IANA also performs DNS root zone management. IANA operates with the help of International Engineering Task Force (IETF) and RFC Editor to manage IP address allocation and DNS root zone management. There are Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) through which IANA allocates local registrations of IP addresses to different regions of the world. Each RIR handles a specific region of the world. Objective:Network Fundamentals Sub-Objective:Describe the need for private IPv4 addressing References:http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc1918.txthttp://www.iana.org/ The range 192.255.255.255 - 193.0.0.0 is a valid public IP address range, not a private IP address range.
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) has reserved the following three ranges for private Internet use:
10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 (10.0.0.0/8)
172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255 (172.16.0.0/12)
192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 (192.168.0.0/16)
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) manages and distributes global public IP addresses. IANA also performs DNS root zone management. IANA operates with the help of International Engineering Task Force (IETF) and RFC Editor to manage IP address allocation and DNS root zone management. There are Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) through which IANA allocates local registrations of IP addresses to different regions of the world. Each RIR handles a specific region of the world.
Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Describe the need for private IPv4 addressing
References:
http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc1918.txt
http://www.iana.org/
Question 3
Which of the following protocols allow the root switch location to be optimized per VLAN? (Choose all that apply.)
- PVST+
- RSTP
- PVRST
- STP
Correct answer: AC
Explanation:
Both Per VLAN Spanning Tree Plus (PVST+) and Per VLAN Rapid Spanning Tree (PVRST) protocols allow for a spanning tree instance for each VLAN, allowing for the location optimization of the root bridge for each VLAN. These are Cisco proprietary enhancements to the 802.1d and 802.1w standards, respectively. Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) is another name for the 802.1w standard. It supports only one instance of spanning tree. Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is another name for the 802.1d standard. It supports only one instance of spanning tree. Objective:LAN Switching Fundamentals Sub-Objective:Configure, verify, and troubleshoot STP protocols References:Cisco Home > Support > Technology Support > LAN Switching Both Per VLAN Spanning Tree Plus (PVST+) and Per VLAN Rapid Spanning Tree (PVRST) protocols allow for a spanning tree instance for each VLAN, allowing for the location optimization of the root bridge for each VLAN.
These are Cisco proprietary enhancements to the 802.1d and 802.1w standards, respectively.
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) is another name for the 802.1w standard. It supports only one instance of spanning tree.
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is another name for the 802.1d standard. It supports only one instance of spanning tree.
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot STP protocols
References:
Cisco Home > Support > Technology Support > LAN Switching
Question 4
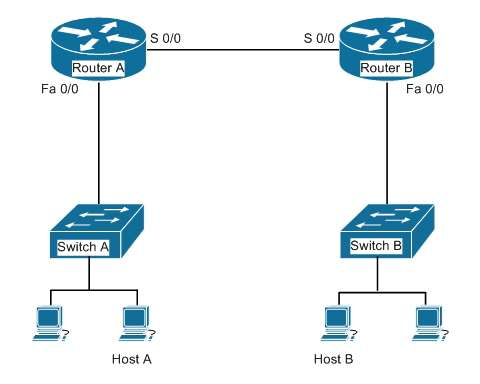
Your assistant just finished configuring a small test network as part of his training. The network is configured as shown in the diagram below:

When testing the configuration, you find that Host A in the diagram cannot ping Host B.
Which of the following pairs of connections are required to be in the same subnet for Host A to be able to ping Host B? (Choose all that apply.)
- The IP address of Host A and the IP address of the Fa0/0 interface of Router A
- The IP address of the Fa0/0 interface of Router A and the IP address of the Fa0/0 interface of Router B
- The IP address of Host A and the IP address of the Fa0/0 interface of Router B
- The IP address of Host A and the IP address of Switch A
- The IP address of the S 0/0 interface of Router A and the IP address of the S 0/0 interface of Router B
- The IP address of Host A and the IP address of Host B
- The IP address of Host B and the IP address of the Fa0/0 interface of Router B
Correct answer: AEG
Explanation:
The following pairs of connections are required to be in the same subnet:the IP address of Host A and the IP address of the Fa0/0 interface of Router A the IP address of the S 0/0 interface of Router A and the IP address of the S 0/0 interface of Router B the IP address of Host B and the IP address of the Fa0/0 interface of Router B When troubleshooting a correctly labeled network diagram for IP addressing problems, one must start on one end and trace each link in one direction, ensuring at each step that the interfaces are in the same subnet. A switch simply passes the packet to the router; therefore, the IP address of the switch is not important. It performs its job even if it has no IP address. Moving from Host A to Host B, however, the following links must be in the same subnet:The IP address of Host A and the IP address of the Fa0/0 interface of Router A The IP address of the S0/0 interface of Router A and the IP address of the S0/0 interface of Router B The IP address of Host B and the IP address of the Fa0/0 interface of Router B Neither of the switch addresses is important to the process. If all other routing issues are correct, it is also not required for Host A and Host B to be in the same subnet. Objective:Network Fundamentals Sub-Objective:Configure, verify, and troubleshoot IPv4 addressing and subnetting References:Cisco > Home > Support > Technology Support > IP > IP Routing > Design > Design Technotes > IP Addressing and Subnetting for New Users The following pairs of connections are required to be in the same subnet:
- the IP address of Host A and the IP address of the Fa0/0 interface of Router A
- the IP address of the S 0/0 interface of Router A and the IP address of the S 0/0 interface of Router B
- the IP address of Host B and the IP address of the Fa0/0 interface of Router B
When troubleshooting a correctly labeled network diagram for IP addressing problems, one must start on one end and trace each link in one direction, ensuring at each step that the interfaces are in the same subnet. A switch simply passes the packet to the router; therefore, the IP address of the switch is not important. It performs its job even if it has no IP address.
Moving from Host A to Host B, however, the following links must be in the same subnet:
- The IP address of Host A and the IP address of the Fa0/0 interface of Router A
- The IP address of the S0/0 interface of Router A and the IP address of the S0/0 interface of Router B
- The IP address of Host B and the IP address of the Fa0/0 interface of Router B
Neither of the switch addresses is important to the process.
If all other routing issues are correct, it is also not required for Host A and Host B to be in the same subnet.
Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot IPv4 addressing and subnetting
References:
Cisco > Home > Support > Technology Support > IP > IP Routing > Design > Design Technotes > IP Addressing and Subnetting for New Users
Question 5
Click and drag the components on the left to their corresponding layers of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model on the right.
Correct answer: To work with this question, an Exam Simulator is required.
Explanation:
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) and Telnet are services, which are implemented at the Application layer in the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model. The Application layer is responsible for interacting directly with the application. It provides application services, such as e-mail. Motion Picture Experts Group (MPEG) and Tagged Image File Format (TIFF) are graphic image formats, which are implemented at the Presentation layer. The Presentation layer enables coding and conversion functions for application layer data. Data is formatted and encrypted at this layer. The Presentation layer converts data into a format which is acceptable to the Application layer. The following are also OSI layers and their descriptions:Session: Used to create, manage, and terminate sessions between communicating nodes. The Session layer handles the service requests and service responses which take place between different applications. Transport: Responsible for error-free and sequential delivery of data. This layer is used to manage data transmission between devices, a process known as flow control. The Transport layer protocols are Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP). Network: Used to define the network address or the Internet Protocol (IP) address, which is then used by the routers to make routing decisions. Data Link: Ensures the reliable transmission of data across a network on the basis of Layer 2 addresses such as MAC addresses (Ethernet) or DLCIs (Frame relay). Physical: Consists of hardware for sending and receiving data on a carrier. The protocols which work at the Physical layer include Fast Ethernet, RS232 and Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM). Objective:Network Fundamentals Sub-Objective:Compare and contrast OSI and TCP/IP models References:Internetworking Technology Handbook > Internetworking Basics > OSI Model and Communication Between Systems File Transfer Protocol (FTP) and Telnet are services, which are implemented at the Application layer in the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model. The Application layer is responsible for interacting directly with the application. It provides application services, such as e-mail.
Motion Picture Experts Group (MPEG) and Tagged Image File Format (TIFF) are graphic image formats, which are implemented at the Presentation layer. The Presentation layer enables coding and conversion functions for application layer data. Data is formatted and encrypted at this layer. The Presentation layer converts data into a format which is acceptable to the Application layer.
The following are also OSI layers and their descriptions:
- Session: Used to create, manage, and terminate sessions between communicating nodes. The Session layer handles the service requests and service responses which take place between different applications.
- Transport: Responsible for error-free and sequential delivery of data. This layer is used to manage data transmission between devices, a process known as flow control. The Transport layer protocols are Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP).
- Network: Used to define the network address or the Internet Protocol (IP) address, which is then used by the routers to make routing decisions.
- Data Link: Ensures the reliable transmission of data across a network on the basis of Layer 2 addresses such as MAC addresses (Ethernet) or DLCIs (Frame relay).
- Physical: Consists of hardware for sending and receiving data on a carrier. The protocols which work at the Physical layer include Fast Ethernet, RS232 and Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM).
Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Compare and contrast OSI and TCP/IP models
References:
Internetworking Technology Handbook > Internetworking Basics > OSI Model and Communication Between Systems
Question 6
Which two fields are present in the output of the show ip interface brief command? (Choose two.)
- YES?
- Helper address
- OK?
- Method
- Proxy ARP
Correct answer: CD
Explanation:
Sample output of the show ip interface brief command is as follows:Router# show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Ethernet0 10.108.00.5 YES NVRAM up up Ethernet1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down Loopback0 10.108.200.5 YES NVRAM up up Serial0 10.108.100.5 YES NVRAM up up Serial1 10.108.40.5 YES NVRAM up up Serial2 10.108.100.5 YES manual up up Serial3 unassigned YES unset administratively down down The following fields are present in the output of the show ip interface brief command:OK?: If the value of this field is "yes", it represents that the IP address is valid. If the value of this field is "No", it represents an invalid IP address. Method: This field can have one of the following values:RARP or SLARP: Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) or Serial Line Address Resolution Protocol (SLARP) request BOOTP: Bootstrap protocolTFTP: Configuration file obtained from TFTP serverManual: Manually changed by CLI commandNVRAM: Configuration file in NVRAMIPCP: ip address negotiated commandDHCP: ip address dhcp commandunassigned: No IP addressunset: Unsetother: UnknownInterface: Refers to the type of interface.IP-Address: Refers to the IP address assigned to the interface.Status: Displays the interface status. Possible values in this field are as follows:up: Interface is administratively up.down: Interface is down.administratively down: Interface is administratively down.Protocol: An indicator of the operational status of the routing protocol for this interface.YES? is not a valid field in the output of the show ip interface brief command. Helper address and Proxy ARP fields are present in the output of the show ip interface command, not the show ip interface brief command. Objective:Network Fundamentals Sub-Objective:Configure, verify, and troubleshoot IPv4 addressing and subnetting References:Cisco > Cisco IOS IP Addressing Command Reference > show ip interface Sample output of the show ip interface brief command is as follows:
Router# show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Ethernet0 10.108.00.5 YES NVRAM up up
Ethernet1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Loopback0 10.108.200.5 YES NVRAM up up
Serial0 10.108.100.5 YES NVRAM up up
Serial1 10.108.40.5 YES NVRAM up up
Serial2 10.108.100.5 YES manual up up
Serial3 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
The following fields are present in the output of the show ip interface brief command:
OK?: If the value of this field is "yes", it represents that the IP address is valid. If the value of this field is "No", it represents an invalid IP address.
Method: This field can have one of the following values:
- RARP or SLARP: Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) or Serial Line Address Resolution Protocol (SLARP) request
- BOOTP: Bootstrap protocol
- TFTP: Configuration file obtained from TFTP server
- Manual: Manually changed by CLI command
- NVRAM: Configuration file in NVRAM
- IPCP: ip address negotiated command
- DHCP: ip address dhcp command
- unassigned: No IP address
- unset: Unset
- other: Unknown
- Interface: Refers to the type of interface.
- IP-Address: Refers to the IP address assigned to the interface.
Status: Displays the interface status. Possible values in this field are as follows:
- up: Interface is administratively up.
- down: Interface is down.
- administratively down: Interface is administratively down.
Protocol: An indicator of the operational status of the routing protocol for this interface.
YES? is not a valid field in the output of the show ip interface brief command.
Helper address and Proxy ARP fields are present in the output of the show ip interface command, not the show ip interface brief command.
Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot IPv4 addressing and subnetting
References:
Cisco > Cisco IOS IP Addressing Command Reference > show ip interface
Question 7
Which two modes are Cisco Internetwork Operating System (IOS) operating modes? (Choose two.)
- User Privileged mode
- User EXEC mode
- Local configuration mode
- Global configuration mode
- NVRAM monitor mode
Correct answer: BD
Explanation:
User EXEC mode and global configuration mode are the Cisco IOS operating modes. The following list shows the Cisco IOS operating modes along with their description:User EXEC mode: The commands in this mode are used to enable connections to remote devices and change the terminal settings for a short duration. User EXEC commands also enable you to perform basic tests and view system information. Global configuration mode: The commands in this mode enable you to make changes to the entire system.Privileged EXEC mode: The commands in this mode are used to configure operating parameters. This mode also provides access to the remaining command modes. Interface configuration mode: The commands in this mode allow you to change the operation for interfacessuch as serial or Ethernet ports. ROM monitor: The commands in this mode are used to perform low-level diagnostics. All the other options are incorrect because they are not valid Cisco IOS operating modes. To enter privileged EXEC mode, you must enter the command enable on the router. You will then be prompted for the enable password, if one has been created. To enter global configuration mode, you must first enter privileged EXEC mode (see above) and then enter the command configure terminal (which can be abbreviated to config t), and the router will enter a mode that allows you to make global configuration changes. Objective:Network Fundamentals Sub-Objective:Select the appropriate cabling type based on implementation requirements References:Cisco Documentation > RPM Installation and Configuration > IOS and Configuration Basics > Cisco IOS Modes of Operation User EXEC mode and global configuration mode are the Cisco IOS operating modes. The following list shows the Cisco IOS operating modes along with their description:
- User EXEC mode: The commands in this mode are used to enable connections to remote devices and change the terminal settings for a short duration. User EXEC commands also enable you to perform basic tests and view system information.
- Global configuration mode: The commands in this mode enable you to make changes to the entire system.
- Privileged EXEC mode: The commands in this mode are used to configure operating parameters. This mode also provides access to the remaining command modes.
- Interface configuration mode: The commands in this mode allow you to change the operation for interfacessuch as serial or Ethernet ports.
- ROM monitor: The commands in this mode are used to perform low-level diagnostics.
All the other options are incorrect because they are not valid Cisco IOS operating modes.
To enter privileged EXEC mode, you must enter the command enable on the router. You will then be prompted for the enable password, if one has been created.
To enter global configuration mode, you must first enter privileged EXEC mode (see above) and then enter the command configure terminal (which can be abbreviated to config t), and the router will enter a mode that allows you to make global configuration changes.
Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Select the appropriate cabling type based on implementation requirements
References:
Cisco Documentation > RPM Installation and Configuration > IOS and Configuration Basics > Cisco IOS Modes of Operation
Question 8

Which of the following accurately describes the purpose of a trunk?
- A trunk is used to carry traffic for a single VLAN and is typically used between switches.
- A trunk is used to carry traffic for a single VLAN and is typically used between a switch and an end-user device.
- A trunk is used to carry multiple VLANs and is typically used between switches.
- A trunk is used to carry multiple VLANs and is typically used between a switch and a server.
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
Trunk links are used between switches to allow communications between hosts that are in the same VLAN, but connected to different switches. Trunk links do not allow hosts in different VLANs to communicate, unless there is an additional trunk link connecting to a Layer 3 device, such as a router or a multilayer switch. Trunk links do allow a host in VLAN 10 on SwitchA to communicate with a host in VLAN 10 on SwitchB. Similarly, a host in VLAN 20 on SwitchA could also communicate with a host in VLAN 20 on SwitchB. A trunk link supports all VLANs by default, and frames that are not traveling on the native VLAN are "tagged" with the VLAN ID of the originating port before being sent over the trunk. The receiving switch reads the VLAN ID and forwards the frame to the appropriate host in the same VLAN. The other options are incorrect because trunk links do not carry data for a single VLAN, nor are trunks used between switches and hosts (such as workstations and servers). When a trunk link is extended to a router for the purpose of enabling routing between VLANs, the physical connection that the link connects to is usually subdivided logically into subinterfaces. Then each subinterface is given an IP address from the same subnet as the computers that reside on that VLAN. Finally, each computer in the VLAN will use the corresponding IP address on the matching subinterface of the router as its default gateway. In the example below, the switch has five VLANs created and some hosts connected to it. If hosts from different VLANs need to communicate, the link between the router and the switch must be a trunk link. Furthermore, the physical link on the router must be subdivided into subinterfaces and addressed according to the legend shown for each subinterface in the diagram. For example, the configuration for VLAN 10 shown in the diagram would be as follows:Router(config)# interface f0/0.10 Router(config-if)#encapsulation dot1q 10 Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.10.254 255.255.255.0 Finally, each computer in VLAN 10 should have its default gateway set to 192.168.10.254. Objective:LAN Switching Fundamentals Sub-Objective:Describe and verify switching concepts Trunk links are used between switches to allow communications between hosts that are in the same VLAN, but connected to different switches. Trunk links do not allow hosts in different VLANs to communicate, unless there is an additional trunk link connecting to a Layer 3 device, such as a router or a multilayer switch. Trunk links do allow a host in VLAN 10 on SwitchA to communicate with a host in VLAN 10 on SwitchB. Similarly, a host in VLAN 20 on SwitchA could also communicate with a host in VLAN 20 on SwitchB. A trunk link supports all VLANs by default, and frames that are not traveling on the native VLAN are "tagged" with the VLAN ID of the originating port before being sent over the trunk. The receiving switch reads the VLAN ID and forwards the frame to the appropriate host in the same VLAN.
The other options are incorrect because trunk links do not carry data for a single VLAN, nor are trunks used between switches and hosts (such as workstations and servers).
When a trunk link is extended to a router for the purpose of enabling routing between VLANs, the physical connection that the link connects to is usually subdivided logically into subinterfaces. Then each subinterface is given an IP address from the same subnet as the computers that reside on that VLAN. Finally, each computer in the VLAN will use the corresponding IP address on the matching subinterface of the router as its default gateway. In the example below, the switch has five VLANs created and some hosts connected to it. If hosts from different VLANs need to communicate, the link between the router and the switch must be a trunk link.

Furthermore, the physical link on the router must be subdivided into subinterfaces and addressed according to the legend shown for each subinterface in the diagram. For example, the configuration for VLAN 10 shown in the diagram would be as follows:
Router(config)# interface f0/0.10
Router(config-if)#encapsulation dot1q 10
Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.10.254 255.255.255.0
Finally, each computer in VLAN 10 should have its default gateway set to 192.168.10.254.
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Describe and verify switching concepts
Question 9
Which Ethernet LAN contention or access method listens for a signal on the channel before transmitting data, and stops transmitting if a collision is detected?
- CSMA/CA
- CSMA/CD
- CSMA/CB
- CSMA/CS
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
The Carrier Sense Multiple Access - Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) contention method verifies that a channel is clear before transmitting, and stops transmitting data when it detects a collision on the channel in use. Carrier Sense Multiple Access (CSMA) is the channel access mechanism used by Ethernet LANs. CSMA defines when and how to access the channel to transmit data. There are two variants of CSMA: CSMA withCollision Avoidance (CSMA/CA) and CSMA/CD. With CSMA/CD, the transmitting station waits to detect channel traffic before sending the first packet over the channel. If the channel happens to be idle, the station transmits its packets. Despite the process of checking the channel before transmitting, it is still possible for two stations to transmit at once, resulting in collisions. If a collision occurs, the transmitting stations perform a retransmission. This retransmission uses a back-off algorithm by which a station waits for a random amount of time before retransmitting. As soon there is a collision on the network, the transmitting station stops transmitting and waits for a random interval of time before attempting the transmission again. You should not select CSMA/CA. With Carrier Sense Multiple Access - Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA), the transmitting station listens for a signal on the channel, then only transmits when the channel is idle. If the channel is busy, it waits a random amount of time before re-attempting transmission. CSMA/CA protocol is used in 802.11-based wireless LANs, while CSMA/CD is used in Ethernet LANs. Collisions are more often avoided with CSMA/CA than with CSMA/CD because sending stations signal non-sending stations to "wait" a specific amount of time and then check for clearance again before sending. The cost of these mechanisms is reduced throughput. CSMA/CB and CSMA/CS are invalid Ethernet contention methods, and are therefore incorrect options. Objective:LAN Switching Fundamentals Sub-Objective:Describe and verify switching concepts References:Cisco Documentation > Internetwork Troubleshooting Handbook > Troubleshooting Ethernet Cisco > Tech Notes > Troubleshooting Ethernet Collisions > Document ID: 12768Cisco > Technology Support > Ethernet > Carrier Sense Multi-Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) The Carrier Sense Multiple Access - Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) contention method verifies that a channel
is clear before transmitting, and stops transmitting data when it detects a collision on the channel in use.
Carrier Sense Multiple Access (CSMA) is the channel access mechanism used by Ethernet LANs. CSMA
defines when and how to access the channel to transmit data. There are two variants of CSMA: CSMA with
Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA) and CSMA/CD.
With CSMA/CD, the transmitting station waits to detect channel traffic before sending the first packet over the channel. If the channel happens to be idle, the station transmits its packets. Despite the process of checking the channel before transmitting, it is still possible for two stations to transmit at once, resulting in collisions. If a collision occurs, the transmitting stations perform a retransmission. This retransmission uses a back-off algorithm by which a station waits for a random amount of time before retransmitting. As soon there is a collision on the network, the transmitting station stops transmitting and waits for a random interval of time before attempting the transmission again.
You should not select CSMA/CA. With Carrier Sense Multiple Access - Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA), the transmitting station listens for a signal on the channel, then only transmits when the channel is idle. If the channel is busy, it waits a random amount of time before re-attempting transmission. CSMA/CA protocol is used in 802.11-based wireless LANs, while CSMA/CD is used in Ethernet LANs. Collisions are more often avoided with CSMA/CA than with CSMA/CD because sending stations signal non-sending stations to "wait" a specific amount of time and then check for clearance again before sending. The cost of these mechanisms is reduced throughput.
CSMA/CB and CSMA/CS are invalid Ethernet contention methods, and are therefore incorrect options.
Objective:
LAN Switching Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Describe and verify switching concepts
References:
Cisco Documentation > Internetwork Troubleshooting Handbook > Troubleshooting Ethernet
Cisco > Tech Notes > Troubleshooting Ethernet Collisions > Document ID: 12768
Cisco > Technology Support > Ethernet > Carrier Sense Multi-Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD)
Question 10
What will be the effects of executing the following set of commands? (Choose all that apply.)
router(config)# router eigrp 44
router (config-router)# network 10.0.0.0
router (config-router)# network 192.168.5.0
- EIGRP will be enabled in AS 44
- EIGRP instance number 44 will be enabled
- EIGRP will be activated on the router interface 10.0.0.2/8
- EIGRP will be activated on the router interface 192.168.5.9/24
- EIGRP will be activated on the router interface 10.0.5.8/16
- EIGRP will be activated on the router interface 192.168.6.1/24
Correct answer: ACDE
Explanation:
The effects of executing this set of commands will be that Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) will be enabled in Autonomous System (AS) 44 and will be active on the router interfaces 10.0.0.2/8,192.168.5.9/24, and 10.0.5.8/16. The router eigrp 10 command is used to enable EIGRP on a router. The network 10.0.0.0 and network 192.168.5.0 commands are used to activate EIGRP over any interfaces that fall within the major networks 10.0.0.0 and 192.168.5.0, or within any subnets of these classful networks. The network commands in EIGRP configuration ignore any subnet-specific information by default. Since the IP address 10.0.5.8.9/24 is in a subnet of the Class A IP network 10.0.0.0, and only the first octet (byte) of a Class A IP address represents the major (classful) network, the remaining bytes are ignored by the network command. EIGRP instance number 44 will not be enabled. The number 44 in the command does not represent an instance of EIGRP; it represents an autonomous system (AS) number. The autonomous-system parameter of the router eigrp command (router eigrp 44) specifies the autonomous system number. To ensure that all the routers in a network can communicate with each other, you should specify the same autonomous system number on all routers. EIGRP will not be activated on the router interface 192.168.6.1/24. This interface does not exist within the Class C network 192.198.5.0 or Class A network 10.0.0.0, or within any of their subnets. Objective:Routing Fundamentals Sub-Objective:Configure, verify, and troubleshoot EIGRP for IPv4 (excluding authentication, filtering, manual summarization, redistribution, stub) References:Cisco > Support > Cisco IOS Software > Configuring EIGRP > Enabling EIGRP CCNA ICND2 Official Exam Certification Guide (Cisco Press, ISBN 1-58720-181-X), Chapter 10: EIGRP, pp.389-390. The effects of executing this set of commands will be that Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) will be enabled in Autonomous System (AS) 44 and will be active on the router interfaces 10.0.0.2/8,192.168.5.9/24, and 10.0.5.8/16.
The router eigrp 10 command is used to enable EIGRP on a router. The network 10.0.0.0 and network 192.168.5.0 commands are used to activate EIGRP over any interfaces that fall within the major networks 10.0.0.0 and 192.168.5.0, or within any subnets of these classful networks. The network commands in EIGRP configuration ignore any subnet-specific information by default. Since the IP address 10.0.5.8.9/24 is in a subnet of the Class A IP network 10.0.0.0, and only the first octet (byte) of a Class A IP address represents the major (classful) network, the remaining bytes are ignored by the network command.
EIGRP instance number 44 will not be enabled. The number 44 in the command does not represent an instance of EIGRP; it represents an autonomous system (AS) number. The autonomous-system parameter of the router eigrp command (router eigrp 44) specifies the autonomous system number. To ensure that all the routers in a network can communicate with each other, you should specify the same autonomous system number on all routers.
EIGRP will not be activated on the router interface 192.168.6.1/24. This interface does not exist within the Class C network 192.198.5.0 or Class A network 10.0.0.0, or within any of their subnets.
Objective:
Routing Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot EIGRP for IPv4 (excluding authentication, filtering, manual summarization, redistribution, stub)
References:
Cisco > Support > Cisco IOS Software > Configuring EIGRP > Enabling EIGRP
CCNA ICND2 Official Exam Certification Guide (Cisco Press, ISBN 1-58720-181-X), Chapter 10: EIGRP, pp.389-390.

