File Info
| Exam | Cisco Certified Network Associate (200-301 CCNA) |
| Number | 200-301 |
| File Name | Cisco.200-301.Marks4Sure.2022-05-19.440q.vcex |
| Size | 23 MB |
| Posted | May 19, 2022 |
| Downloads: | 2 |
| Download | Cisco.200-301.Marks4Sure.2022-05-19.440q.vcex |
How to open VCEX & EXAM Files?
Files with VCEX & EXAM extensions can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Coupon: MASTEREXAM
With discount: 20%





Demo Questions
Question 1
How do TCP and UDP differ in the way they guarantee packet delivery?
- TCP uses checksum, acknowledgement, and retransmissions, and UDP uses checksums only.
- TCP uses two-dimensional parity checks, checksums, and cyclic redundancy checks and UDP uses retransmissions only.
- TCP uses checksum, parity checks, and retransmissions, and UDP uses acknowledgements only.
- TCP uses retransmissions, acknowledgement and parity checks and UDP uses cyclic redundancy checks only.
Correct answer: A
Question 2

Refer to the exhibit.

If the network environment is operating normally, which type of device must be connected to interface FastEthernet 0/1?
- DHCP client
- access point
- router
- PC
Correct answer: C
Question 3
How do TCP and UDP differ in the way that they establish a connection between two endpoints?
- TCP uses synchronization packets, and UDP uses acknowledgment packets.
- UDP uses SYN, SYN ACK and FIN bits in the frame header while TCP uses SYN, SYN ACK and ACK bits
- UDP provides reliable message transfer and TCP is a connectionless protocol
- TCP uses the three-way handshake and UDP does not guarantee message delivery
Correct answer: D
Question 4
Which CRUD operation corresponds to the HTTP GET method?
- read
- update
- create
- delete
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
GET: This method retrieves the information identified by the request URI. In the context of the RESTful web services, this method is used to retrieve resources. This is the method used for read operations (the R in CRUD). https://hub.packtpub.com/crud-operations-rest/ GET: This method retrieves the information identified by the request URI. In the context of the RESTful web services, this method is used to retrieve resources.
This is the method used for read operations (the R in CRUD).
https://hub.packtpub.com/crud-operations-rest/
Question 5
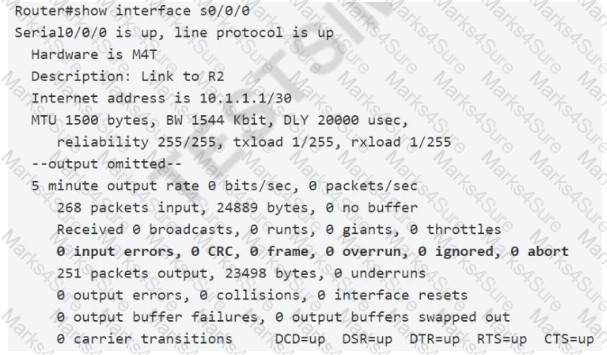
A frame that enters a switch fails the Frame Check Sequence. Which two interface counters are incremented? (Choose two)
- runts
- giants
- frame
- CRC
- input errors
Correct answer: DE
Explanation:
Whenever the physical transmission has problems, the receiving device might receive a frame whose bits have changed values. These frames do not pass the error detection logic as implemented in the FCS field in the Ethernet trailer. The receiving device discards the frame and counts it as some kind of input error. Cisco switches list this error as a CRC error. Cyclic redundancy check (CRC) is a term related to how the FCS math detects an error. The “input errors” includes runts, giants, no buffer, CRC, frame, overrun, and ignored counts. The output below show the interface counters with the “show interface s0/0/0” command: Whenever the physical transmission has problems, the receiving device might receive a frame whose bits have changed values. These frames do not pass the error detection logic as implemented in the FCS field in the Ethernet trailer. The receiving device discards the frame and counts it as some kind of input error.
Cisco switches list this error as a CRC error. Cyclic redundancy check (CRC) is a term related to how the FCS math detects an error.
The “input errors” includes runts, giants, no buffer, CRC, frame, overrun, and ignored counts.
The output below show the interface counters with the “show interface s0/0/0” command:

Question 6
What is the benefit of using FHRP?
- reduced management overhead on network routers
- balancing traffic across multiple gateways in proportion to their loads
- higher degree of availability
- reduced ARP traffic on the network
Correct answer: C
Question 7
Which switch technology establishes a network connection immediately when it is plugged in?
- PortFast
- BPDU guard
- UplinkFast
- BackboneFast
Correct answer: C
Question 8
What is the role of a firewall in an enterprise network?
- Forwards packets based on stateless packet inspection
- Processes unauthorized packets and allows passage to less secure segments of the network
- determines which packets are allowed to cross from unsecured to secured networks
- explicitly denies all packets from entering an administrative domain
Correct answer: C
Question 9
Which command enables a router to become a DHCP client?
- ip address dhcp
- ip helper-address
- ip dhcp pool
- ip dhcp client
Correct answer: A
Question 10
What facilitates a Telnet connection between devices by entering the device name?
- SNMP
- DNS lookup
- syslog
- NTP
Correct answer: B

