File Info
| Exam | Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (300-410 ENARSI) |
| Number | 300-410 |
| File Name | Cisco.300-410.CertDumps.2020-11-11.100q.vcex |
| Size | 14 MB |
| Posted | Nov 11, 2020 |
| Download | Cisco.300-410.CertDumps.2020-11-11.100q.vcex |
How to open VCEX & EXAM Files?
Files with VCEX & EXAM extensions can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Coupon: MASTEREXAM
With discount: 20%





Demo Questions
Question 1

Refer to the exhibit. AAA server 10.1.1.1 is configured with the default authentication and accounting settings, but the switch cannot communicate with the server. Which action resolves this issue?

- Correct the timeout value
- Match the authentication port
- Correct the shared secret
- Match the accounting port
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
By default, RADIUS uses UDP port 1812 for authentication and port 1813 for accounting. In the exhibit above we see port 1814 is being used for authentication to AAA server at 10.1.1.1 which is not the default port so we must adjust the authentication port to the default value 1812. By default, RADIUS uses UDP port 1812 for authentication and port 1813 for accounting. In the exhibit above we see port 1814 is being used for authentication to AAA server at 10.1.1.1 which is not the default port so we must adjust the authentication port to the default value 1812.
Question 2
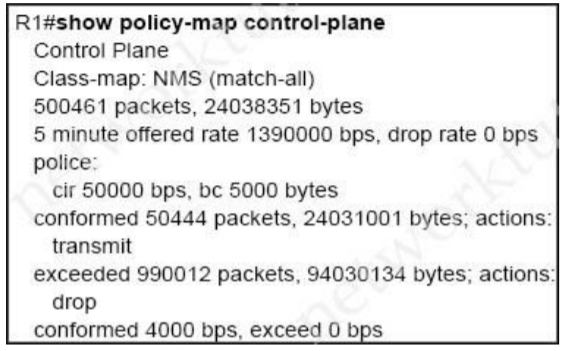
Refer to the exhibit. A company is evaluating multiple network management system tools. Trending graphs generated by SNMP data are returned by the NMS and appear to have multiple gaps. While troubleshooting the issue, an engineer noticed the relevant output. What solves the gaps in the graphs?

- Remove the class map NMS from being part of control plane policing
- Remove the exceed-rate command in the class map
- Configure the CIR rate to a lower value that accommodates all the NMS tools
- Separate the NMS class map in multiple class maps based on the specific protocols with appropriate CoPP actions
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
The class-map NMS in the exhibit did not classify traffic into specific protocols so many packets were dropped. We should create some class-map to classify the receiving traffic. It is also a recommendation of CoPP/CPP policy:“Developing a CPP policy starts with the classification of the control plane traffic. To that end, the control plane traffic needs to be first identified and separated into different class maps.” Reference: https://ptgmedia.pearsoncmg.com/images/9781587143694/downloads/i9781587143694_app02.pdf The class-map NMS in the exhibit did not classify traffic into specific protocols so many packets were dropped. We should create some class-map to classify the receiving traffic. It is also a recommendation of CoPP/CPP policy:
“Developing a CPP policy starts with the classification of the control plane traffic. To that end, the control plane traffic needs to be first identified and separated into different class maps.”
Reference: https://ptgmedia.pearsoncmg.com/images/9781587143694/downloads/i9781587143694_app02.pdf
Question 3

Drag and drop the credentials from the left onto the remote login information on the right to resolve a failed login attempt to vtys. Not all credentials are used.

Correct answer: To work with this question, an Exam Simulator is required.
Explanation:
vty 0:+ cisco + 0csic vty 1:+ no username + no password The command “aaa authentication login default none” means no authentication is required when access to the device via Console/VTY/AUX so if one interface does not specify another login authentication method (via the “login authentication …” command), it will allow to access without requiring username or password. In this case VTY 1 does not specify another authentication login method so it will use the default method (which is “none” in this case). vty 0:
+ cisco
+ 0csic
vty 1:
+ no username
+ no password
The command “aaa authentication login default none” means no authentication is required when access to the device via Console/VTY/AUX so if one interface does not specify another login authentication method (via the “login authentication …” command), it will allow to access without requiring username or password. In this case VTY 1 does not specify another authentication login method so it will use the default method (which is “none” in this case).
Question 4
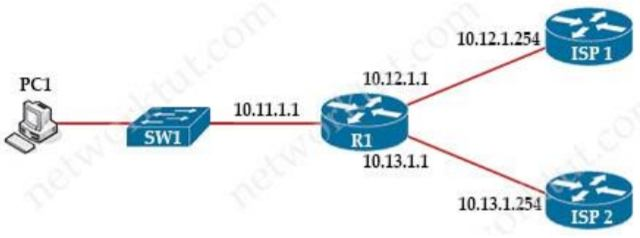

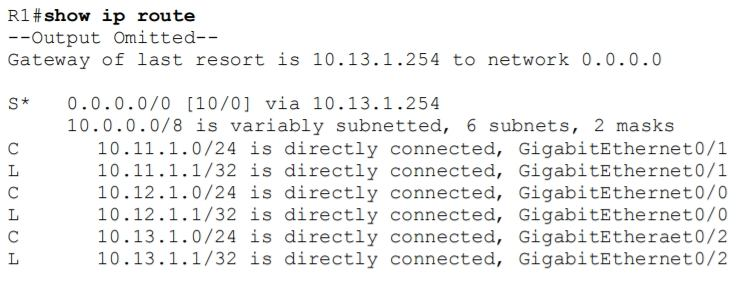
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is monitoring reachability of the configured default routes to ISP1 and ISP2. The default route from ISP1 is preferred if available. How is this issue resolved?



- Use the icmp-echo command to track both default routes
- Start IP SLA by matching numbers for track and ip sla commands
- Start IP SLA by defining frequency and scheduling it
- Use the same AD for both default routes
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
In the above configuration we have not had activated our IP SLA operation. We can start it with this command:R1(config)#ip sla schedule 100 life forever start-time now Also we should specific the rate of ICMP echo:R1(config-ip-sla-echo)#frequency 5 // Send ICMP echo every 5 seconds In the above configuration we have not had activated our IP SLA operation. We can start it with this command:
R1(config)#ip sla schedule 100 life forever start-time now
Also we should specific the rate of ICMP echo:
R1(config-ip-sla-echo)#frequency 5 // Send ICMP echo every 5 seconds
Question 5
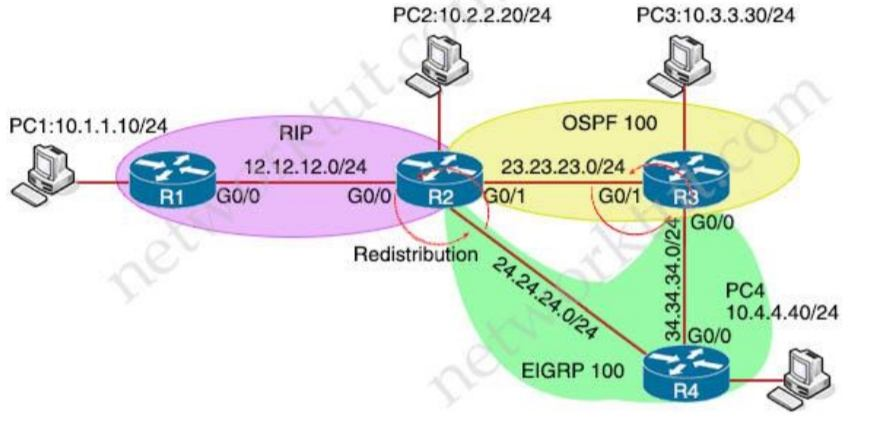

Refer to the exhibit. Redistribution is enabled between the routing protocols, and now PC2 PC3, and PC4 cannot reach PC1. What are the two solutions to fix the problem? (Choose two)
- Filter RIP and OSPF routes back into OSPF from EIGRP when redistributing into OSPF in R2
- Filter all routes except EIGRP routes when redistributing into OSPF in R3
- Filter OSPF routes into RIP from EIGRP when redistributing into RIP in R2
- Filter all routes except RIP routes when redistributing into EIGRP in R2
- Filter RIP routes back into RIP when redistributing into RIP in R2
Correct answer: CE
Explanation:
Even PC2 cannot reach PC1 so there is something wrong with RIP redistribution in R2. Because RIP has higher Administrative Distance (AD) value than OSPF and EIGRP so it will be looped when doing mutual redistribution. Even PC2 cannot reach PC1 so there is something wrong with RIP redistribution in R2. Because RIP has higher Administrative Distance (AD) value than OSPF and EIGRP so it will be looped when doing mutual redistribution.
Question 6
Which label operations are performed by a label edge router?
- PUSH and PHP
- SWAP and POP
- SWAP and PUSH
- PUSH and POP
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
The entry and exit routers of an MPLS network are called edge LSR (or label edge routers – LER), which, respectively, inject (push) an MPLS label onto an incoming packet (label assignment) and remove (pop) it off the outgoing packet (label removal). The entry and exit routers of an MPLS network are called edge LSR (or label edge routers – LER), which, respectively, inject (push) an MPLS label onto an incoming packet (label assignment) and remove (pop) it off the outgoing packet (label removal).
Question 7
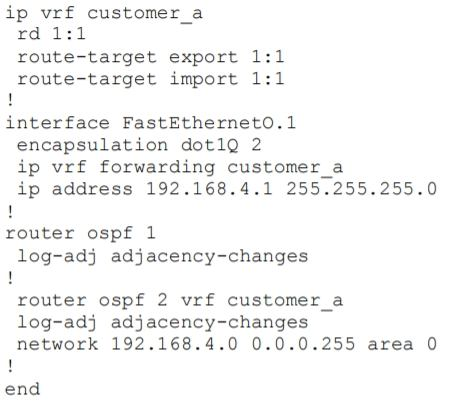
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator configured VRF lite for customer A. The technician at the remote site misconfigured VRF on the router. Which configuration will resolve connectivity for both sites of customer A?

- ip vrf customer_ard 1:2route-target both 1:1
- ip vrf customer_ard 1:2route-target both 1:2
- ip vrf customer_ard 1:1router-target import 1:1router-target export 1:2
- ip vrf customer_ard 1:1route-target export 1:2router-target import 1:2
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
From the exhibit, we learned:+ VRF customer_a was exported with Route target (RT) of 1:1 so at the remote site it must be imported with the same RT 1:1.+ VRF customer_a was imported with Route target (RT) of 1:1 so at the remote site it must be exported with the same RT 1:1.Therefore at the remote site we must configure the command “route-target both 1:1” (which is equivalent to two commands “route-target import 1:1” & “route-target export 1:1”. From the exhibit, we learned:
+ VRF customer_a was exported with Route target (RT) of 1:1 so at the remote site it must be imported with the same RT 1:1.
+ VRF customer_a was imported with Route target (RT) of 1:1 so at the remote site it must be exported with the same RT 1:1.
Therefore at the remote site we must configure the command “route-target both 1:1” (which is equivalent to two commands “route-target import 1:1” & “route-target export 1:1”.
Question 8
Drag and drop the operations from the left onto the locations where the operations are performed on the right.
Correct answer: To work with this question, an Exam Simulator is required.
Explanation:
Label Switch Router:+ Reads the labels and forwards the packet based on the labels + Performs penultimate hop popping Label Edge Router:+ Handles traffic between multiple VPNs + Assigns labels to unlabelled packets Label Switch Router:
+ Reads the labels and forwards the packet based on the labels
+ Performs penultimate hop popping
Label Edge Router:
+ Handles traffic between multiple VPNs
+ Assigns labels to unlabelled packets
Question 9
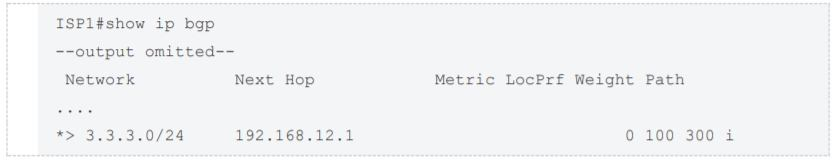
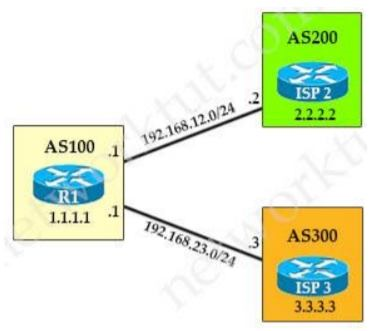
After some changes in the routing policy, it is noticed that the router in AS 45123 is being used as a transit AS router for several service providers. Which configuration ensures that the branch router in AS 45123 advertises only the local networks to all SP neighbors?
- ip as-path access-list 1 permit ^45123$!router bgp 45123neighbor SP-Neighbors filter-list 1 out
- ip as-path access-list 1 permit ^45123!router bgp 45123neighbor SP-Neighbors filter-list 1 out
- ip as-path access-list 1 permit ^$!router bgp 45123neighbor SP-Neighbors filter-list 1 out
- ip as-path access-list 1 permit!router bgp 45123neighbor SP-Neighbors filter-list 1 out
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
By default BGP advertises all prefixes to external BGP neighbors. This means that if you are multihomed (connected to two or more ISPs) then you might become a transit AS. For example, ISP 2 in AS 200 can send traffic to your router in AS 100 to reach ISP 3 in AS 300 because you advertised prefixes in ISP 3 to ISP 2. This is what will be seen in the BGP routing table of ISP1: In order to prevent this we have to ensure that your router only advertises prefixes from its own autonomous system. One of the method to solve this problem is using Filter-list with AS-PATH access-list: R1(config)# ip as-path access-list 1 permit ^$ R1(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.12.2 filter-list 1 out R1(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.23.3 filter-list 1 out It ensures that we will only advertise prefixes from our own AS. The ^$ regular expression ensures that we will only advertise locally originated prefixes. We should apply this filter to both ISPs. By default BGP advertises all prefixes to external BGP neighbors. This means that if you are multihomed (connected to two or more ISPs) then you might become a transit AS. For example, ISP 2 in AS 200 can send traffic to your router in AS 100 to reach ISP 3 in AS 300 because you advertised prefixes in ISP 3 to ISP 2.
This is what will be seen in the BGP routing table of ISP1:

In order to prevent this we have to ensure that your router only advertises prefixes from its own autonomous system. One of the method to solve this problem is using Filter-list with AS-PATH access-list:

R1(config)# ip as-path access-list 1 permit ^$
R1(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.12.2 filter-list 1 out
R1(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.23.3 filter-list 1 out
It ensures that we will only advertise prefixes from our own AS. The ^$ regular expression ensures that we will only advertise locally originated prefixes. We should apply this filter to both ISPs.
Question 10
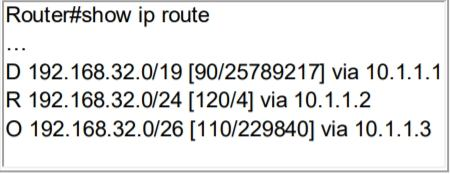
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is trying to get a packet destined for 192.168.32.100 forwarded through 10.1.1.1, but it was forwarded through 10.1.1.2. What action forwards the packets through 10.1.1.1?

- Configure EIGRP to receive 192.168.32.0 route with lower metric
- Configure EIGRP to receive 192.168.32.0 route with lower administrative distance
- Configure EIGRP to receive 192.168.32.0 route with equal or longer prefix than /24
- Configure EIGRP to receive 192.168.32.0 route with longer prefix than /19
Correct answer: C

