File Info
| Exam | Implementing Cisco Enterprise Network Core Technologies (350-401 ENCOR) |
| Number | 350-401 |
| File Name | Cisco.350-401.ITExamAnswers.2022-04-19.536q.tqb |
| Size | 41 MB |
| Posted | Apr 19, 2022 |
| Download | Cisco.350-401.ITExamAnswers.2022-04-19.536q.tqb |
How to open VCEX & EXAM Files?
Files with VCEX & EXAM extensions can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Coupon: MASTEREXAM
With discount: 20%





Demo Questions
Question 1
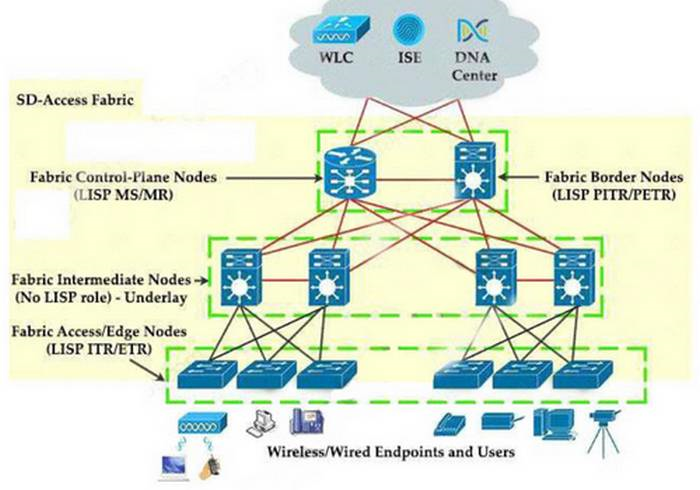
Which function does a fabric edge node perform in an SD-Access deployment?
- Connects endpoints to the fabric and forwards their traffic.
- Encapsulates end-user data traffic into LISP.
- Connects the SD-Access fabric to another fabric or external Layer 3 networks.
- Provides reachability between border nodes in the fabric underlay.
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
There are five basic device roles in the fabric overlay:Control plane node: This node contains the settings, protocols, and mapping tables to provide the endpoint-to-location (EID-to-RLOC) mapping system for the fabric overlay.Fabric border node: This fabric device (for example, core layer device) connects external Layer 3 networks to the SDA fabric.Fabric edge node: This fabric device (for example, access or distribution layer device) connects wired endpoints to the SDA fabric.Fabric WLAN controller (WLC): This fabric device connects APs and wireless endpoints to the SDA fabric.Intermediate nodes: These are intermediate routers or extended switches that do not provide any sort of SD-Access fabric role other than underlay services. There are five basic device roles in the fabric overlay:
- Control plane node: This node contains the settings, protocols, and mapping tables to provide the endpoint-to-location (EID-to-RLOC) mapping system for the fabric overlay.
- Fabric border node: This fabric device (for example, core layer device) connects external Layer 3 networks to the SDA fabric.
- Fabric edge node: This fabric device (for example, access or distribution layer device) connects wired endpoints to the SDA fabric.
- Fabric WLAN controller (WLC): This fabric device connects APs and wireless endpoints to the SDA fabric.
- Intermediate nodes: These are intermediate routers or extended switches that do not provide any sort of SD-Access fabric role other than underlay services.

Question 2

Refer to the exhibit.Which privilege level is assigned to VTY users?

- 1
- 7
- 13
- 15
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
Lines (CON, AUX, VTY) default to level 1 privileges. Lines (CON, AUX, VTY) default to level 1 privileges.
Question 3
What is the difference between a RIB and a FIB?
- The FIB is populated based on RIB content.
- The RIB maintains a minor image of the FIB.
- The RIB is used to make IP source prefix-based switching decisions.
- The FIB is where all IP routing information is stored.
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
CEF uses a Forwarding Information Base (FIB) to make IP destination prefix-based switching decisions. The FIB is conceptually similar to a routing table or information base. It maintains a mirror image of the forwarding information contained in the IP routing table. When routing or topology changes occur in the network, the IP routing table is updated, and those changes are reflected in the FIB. The FIB maintains next-hop address information based on the information in the IP routing table. Because there is a one-to-one correlation between FIB entries and routing table entries, the FIB contains all known routes and eliminates the need for route cache maintenance that is associated with earlier switching paths such as fast switching and optimum switching. Note: In order to view the Routing information base (RIB) table, use the “show ip route” command.To view the Forwarding Information Base (FIB), use the “show ip cef” command. RIB is in Control plane while FIB is in Data plane. CEF uses a Forwarding Information Base (FIB) to make IP destination prefix-based switching decisions. The FIB is conceptually similar to a routing table or information base. It maintains a mirror image of the forwarding information contained in the IP routing table. When routing or topology changes occur in the network, the IP routing table is updated, and those changes are reflected in the FIB. The FIB maintains next-hop address information based on the information in the IP routing table. Because there is a one-to-one correlation between FIB entries and routing table entries, the FIB contains all known routes and eliminates the need for route cache maintenance that is associated with earlier switching paths such as fast switching and optimum switching.
Note: In order to view the Routing information base (RIB) table, use the “show ip route” command.
To view the Forwarding Information Base (FIB), use the “show ip cef” command. RIB is in Control plane while FIB is in Data plane.

