File Info
| Exam | Implementing Cisco Enterprise Network Core Technologies (350-401 ENCOR) |
| Number | 350-401 |
| File Name | Cisco.350-401.NewDumps.2021-09-25.169q.vcex |
| Size | 3 MB |
| Posted | Sep 25, 2021 |
| Download | Cisco.350-401.NewDumps.2021-09-25.169q.vcex |
How to open VCEX & EXAM Files?
Files with VCEX & EXAM extensions can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Coupon: MASTEREXAM
With discount: 20%





Demo Questions
Question 1
When a wired client connects to an edge switch in an SDA fabric, which component decides whether the client has access to the network?
- control-plane node
- Identity Service Engine
- RADIUS server
- edge node
Correct answer: B
Question 2
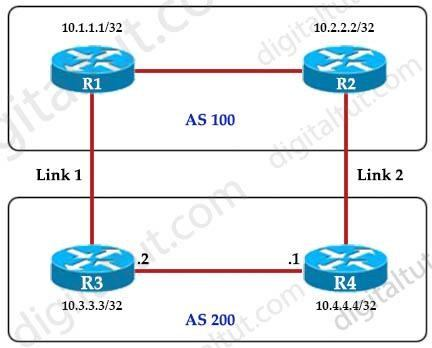
Refer to the exhibit.
An engineer must ensure that all traffic leaving AS 200 will choose Link 2 as the exit point. Assuming that all BGP neighbor relationships have been formed and that the attributes have not been changed on any of the routers, which configuration accomplish task?

- R4(config-router)#bgp default local-preference 200
- R3(config-router)#neighbor 10.1.1.1 weight 200
- R3(config-router)#bgp default local-preference 200
- R4(config-router)#neighbor 10.2.2.2 weight 200
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
Local preference is an indication to the AS about which path has preference to exit the AS in order to reach a certain network. A path with a higher local preference is preferred. The default value for local preference is 100. Unlike the weight attribute, which is only relevant to the local router, local preference is an attribute that routers exchange in the same AS. The local preference is set with the bgp default local-preference value command. In this case, both R3 & R4 have exit links but R4 has higher local-preference so R4 will be chosen as the preferred exit point from AS 200. (Reference:http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a00800c95bb.shtml#lo calpref) Local preference is an indication to the AS about which path has preference to exit the AS in order to reach a certain network. A path with a higher local preference is preferred. The default value for local preference is 100.
Unlike the weight attribute, which is only relevant to the local router, local preference is an attribute that routers exchange in the same AS. The local preference is set with the bgp default local-preference value command.
In this case, both R3 & R4 have exit links but R4 has higher local-preference so R4 will be chosen as the preferred exit point from AS 200.
(Reference:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a00800c95bb.shtml#lo calpref)
Question 3
Which protocol infers that a YANG data model is being used?
- SNMP
- REST
- RESTCONF
- NX-API
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
YANG (Yet Another Next Generation) is a data modeling language for the definition of data sent over network management protocols such as the NETCONF and RESTCONF. YANG (Yet Another Next Generation) is a data modeling language for the definition of data sent over network management protocols such as the NETCONF and RESTCONF.
Question 4
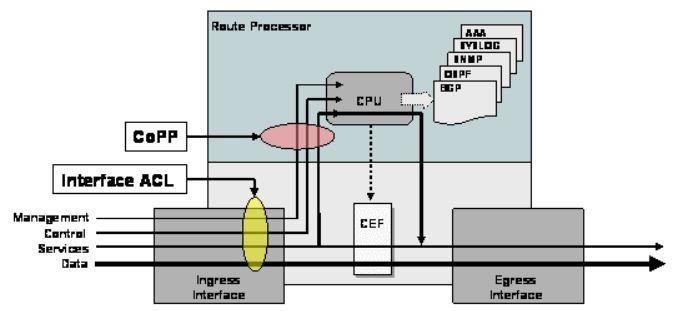
Which configuration restricts the amount of SSH that a router accepts 100 kbps?
- class-map match-all CoPP_SSHmatch access-group name CoPP_SSH!policy-map CoPP_SSHclass CoPP_SSHpolice cir 100000exceed-action drop!!!interface GigabitEthernet0/1ip address 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.0ip access-group CoPP_SSH outduplex autospeed automedia-type rj45service-policy input CoPP_SSH!ip access-list extended CoPP_SSHpermit tcp any any eq 22!
- class-map match-all CoPP_SSHmatch access-group name CoPP_SSH!policy-map CoPP_SSHclass CoPP_SSHpolice cir CoPP_SSHexceed-action drop!!!interface GigabitEthernet0/1ip address 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.0ip access-group ... outduplex autospeed automedia-type rj45service-policy input CoPP_SSH!ip access-list extended CoPP_SSHdeny tcp any any eq 22!
- class-map match-all CoPP_SSHmatch access-group name CoPP_SSH!policy-map CoPP_SSHclass CoPP_SSHpolice cir 100000exceed-action drop!!!control-planeservice-policy input CoPP_SSH!ip access-list extended CoPP_SSHdeny tcp any any eq 22!
- class-map match-all CoPP_SSHmatch access-group name CoPP_SSH!policy-map CoPP_SSHclass CoPP_SSHpolice cir 100000exceed-action drop!!!control-plane transitservice-policy input CoPP_SSH!ip access-list extended CoPP_SSHpermit tcp any any eq 22!
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
CoPP protects the route processor on network devices by treating route processor resources as a separate entity with its own ingress interface (and in some implementations, egress also). CoPP is used to police traffic that is destined to the route processor of the router such as:+ Routing protocols like OSPF, EIGRP, or BGP. + Gateway redundancy protocols like HSRP, VRRP, or GLBP. + Network management protocols like telnet, SSH, SNMP, or RADIUS. Therefore we must apply the CoPP to deal with SSH because it is in the management plane. CoPP must be put under control-plane command. But we cannot name the control-plane (like transit). CoPP protects the route processor on network devices by treating route processor resources as a separate entity with its own ingress interface (and in some implementations, egress also). CoPP is used to police traffic that is destined to the route processor of the router such as:
+ Routing protocols like OSPF, EIGRP, or BGP.
+ Gateway redundancy protocols like HSRP, VRRP, or GLBP. + Network management protocols like telnet, SSH, SNMP, or RADIUS.

Therefore we must apply the CoPP to deal with SSH because it is in the management plane. CoPP must be put under control-plane command. But we cannot name the control-plane (like transit).
Question 5
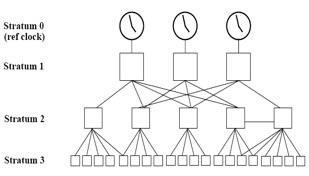
What NTP stratum level is a server that is connected directly to an authoritative time source?
- Stratum 0
- Stratum 1
- Stratum 14
- Stratum 15
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
The stratum levels define the distance from the reference clock. A reference clock is a stratum 0 device that is assumed to be accurate and has little or no delay associated with it. Stratum 0 servers cannot be used on the network but they are directly connected to computers which then operate as stratum-1 servers. A stratum 1 time server acts as a primary network time standard. A stratum 2 server is connected to the stratum 1 server; then a stratum 3 server is connected to the stratum 2 server and so on. A stratum 2 server gets its time via NTP packet requests from a stratum 1 server. A stratum 3 server gets its time via NTP packet requests from a stratum-2 server... A stratum server may also peer with other stratum servers at the same level to provide more stable and robust time for all devices in the peer group (for example a stratum 2 server can peer with other stratum 2 servers). NTP uses the concept of a stratum to describe how many NTP hops away a machine is from an authoritative time source. A stratum 1 time server typically has an authoritative time source (such as a radio or atomic clock, or a Global Positioning System (GPS) time source) directly attached, a stratum 2 time server receives its time via NTP from a stratum 1 time server, and so on. Reference:https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/asr920/configuration/guide/bsm/16-6-1/b- bsm-xe-16-6-1-asr920/bsm-time-calendar-set.html The stratum levels define the distance from the reference clock. A reference clock is a stratum 0 device that is assumed to be accurate and has little or no delay associated with it. Stratum 0 servers cannot be used on the network but they are directly connected to computers which then operate as stratum-1 servers. A stratum 1 time server acts as a primary network time standard.

A stratum 2 server is connected to the stratum 1 server; then a stratum 3 server is connected to the stratum 2 server and so on. A stratum 2 server gets its time via NTP packet requests from a stratum 1 server. A stratum 3 server gets its time via NTP packet requests from a stratum-2 server... A stratum server may also peer with other stratum servers at the same level to provide more stable and robust time for all devices in the peer group (for example a stratum 2 server can peer with other stratum 2 servers).
NTP uses the concept of a stratum to describe how many NTP hops away a machine is from an authoritative time source. A stratum 1 time server typically has an authoritative time source (such as a radio or atomic clock, or a Global Positioning System (GPS) time source) directly attached, a stratum 2 time server receives its time via NTP from a stratum 1 time server, and so on.
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/asr920/configuration/guide/bsm/16-6-1/b- bsm-xe-16-6-1-asr920/bsm-time-calendar-set.html
Question 6
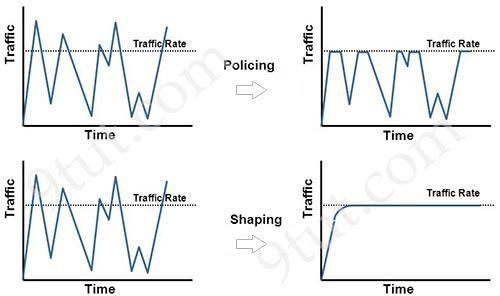
How does QoS traffic shaping alleviate network congestion?
- It drops packets when traffic exceeds a certain bitrate.
- It buffers and queue packets above the committed rate.
- It fragments large packets and queues them for delivery.
- It drops packets randomly from lower priority queues.
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
Traffic shaping retains excess packets in a queue and then schedules the excess for later transmission over increments of time. The result of traffic shaping is a smoothed packet output rate. Traffic shaping retains excess packets in a queue and then schedules the excess for later transmission over increments of time. The result of traffic shaping is a smoothed packet output rate.

Question 7
An engineer is describing QoS to a client. Which two facts apply to traffic policing? (Choose two)
- Policing adapts to network congestion by queuing excess traffic
- Policing should be performed as close to the destination as possible
- Policing drops traffic that exceeds the defined rate
- Policing typically delays the traffic, rather than drops it
- Policing should be performed as close to the source as possible
Correct answer: CE
Explanation:
Traffic policing propagates bursts. When the traffic rate reaches the configured maximum rate (or committed information rate), excess traffic is dropped (or remarked). The result is an output rate that appears as a saw-tooth with crests and troughs. Unlike traffic shaping, traffic policing does not cause delay. Classification (which includes traffic policing, traffic shaping and queuing techniques) should take place at the network edge. It is recommended that classification occur as close to the source of the traffic as possible. Also according to this Cisco link, policing traffic as close to the source as possible. Traffic policing propagates bursts. When the traffic rate reaches the configured maximum rate (or committed information rate), excess traffic is dropped (or remarked). The result is an output rate that appears as a saw-tooth with crests and troughs.
Unlike traffic shaping, traffic policing does not cause delay.
Classification (which includes traffic policing, traffic shaping and queuing techniques) should take place at the network edge. It is recommended that classification occur as close to the source of the traffic as possible.
Also according to this Cisco link, policing traffic as close to the source as possible.
Question 8
What mechanism does PIM use to forward multicast traffic?
- PIM sparse mode uses a pull model to deliver multicast traffic
- PIM dense mode uses a pull model to deliver multicast traffic
- PIM sparse mode uses receivers to register with the RP
- PIM sparse mode uses a flood and prune model to deliver multicast traffic
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
PIM dense mode (PIM-DM) uses a push model to flood multicast traffic to every corner of the network. This push model is a brute-force method of delivering data to the receivers. This method would be efficient in certain deployments in which there are active receivers on every subnet in the network. PIM-DM initially floods multicast traffic throughout the network. Routers that have no downstream neighbors prune the unwanted traffic. This process repeats every 3 minutes. PIM Sparse Mode (PIM-SM) uses a pull model to deliver multicast traffic. Only network segments with active receivers that have explicitly requested the data receive the traffic. PIM- SM distributes information about active sources by forwarding data packets on the shared tree. Because PIM-SM uses shared trees (at least initially), it requires the use of an RP. The RP must be administratively configured in the network. Answer C seems to be correct but it is not, PIM spare mode uses sources (not receivers) to register with the RP. Sources register with the RP, and then data is forwarded down the shared tree to the receivers. Reference: Selecting MPLS VPN Services Book, page 193 PIM dense mode (PIM-DM) uses a push model to flood multicast traffic to every corner of the network. This push model is a brute-force method of delivering data to the receivers. This method would be efficient in certain deployments in which there are active receivers on every subnet in the network. PIM-DM initially floods multicast traffic throughout the network. Routers that have no downstream neighbors prune the unwanted traffic. This process repeats every 3 minutes.
PIM Sparse Mode (PIM-SM) uses a pull model to deliver multicast traffic. Only network segments with active receivers that have explicitly requested the data receive the traffic. PIM- SM distributes information about active sources by forwarding data packets on the shared tree. Because PIM-SM uses shared trees (at least initially), it requires the use of an RP. The RP must be administratively configured in the network.
Answer C seems to be correct but it is not, PIM spare mode uses sources (not receivers) to register with the RP. Sources register with the RP, and then data is forwarded down the shared tree to the receivers.
Reference: Selecting MPLS VPN Services Book, page 193
Question 9
Which two namespaces does the LISP network architecture and protocol use? (Choose two)
- TLOC
- RLOC
- DNS
- VTEP
- EID
Correct answer: BE
Explanation:
Locator ID Separation Protocol (LISP) is a network architecture and protocol that implements the use of two namespaces instead of a single IP address:+ Endpoint identifiers (EIDs)--assigned to end hosts. + Routing locators (RLOCs)--assigned to devices (primarily routers) that make up the global routing system. Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/iproute_lisp/configuration/xe- 3s/irl-xe-3s-book/irl-overview.html Locator ID Separation Protocol (LISP) is a network architecture and protocol that implements the use of two namespaces instead of a single IP address:
+ Endpoint identifiers (EIDs)--assigned to end hosts.
+ Routing locators (RLOCs)--assigned to devices (primarily routers) that make up the global routing system.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/iproute_lisp/configuration/xe- 3s/irl-xe-3s-book/irl-overview.html
Question 10
Which First Hop Redundancy Protocol should be used to meet a design requirements for more efficient default bandwidth usage across multiple devices?
- GLBP
- LCAP
- HSRP
- VRRP
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
The main disadvantage of HSRP and VRRP is that only one gateway is elected to be the active gateway and used to forward traffic whilst the rest are unused until the active one fails. Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) is a Cisco proprietary protocol and performs the similar function to HSRP and VRRP but it supports load balancing among members in a GLBP group. The main disadvantage of HSRP and VRRP is that only one gateway is elected to be the active gateway and used to forward traffic whilst the rest are unused until the active one fails. Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) is a Cisco proprietary protocol and performs the similar function to HSRP and VRRP but it supports load balancing among members in a GLBP group.

