File Info
| Exam | Certified Ethical Hacker v11 Exam |
| Number | 312-50v11 |
| File Name | ECCouncil.312-50v11.ExamCollection.2023-12-29.115q.vcex |
| Size | 321 KB |
| Posted | Dec 29, 2023 |
| Downloads: | 1 |
| Download | ECCouncil.312-50v11.ExamCollection.2023-12-29.115q.vcex |
How to open VCEX & EXAM Files?
Files with VCEX & EXAM extensions can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Coupon: MASTEREXAM
With discount: 20%





Demo Questions
Question 1
Jude, a pen tester working in Keiltech Ltd., performs sophisticated security testing on his company's network infrastructure to identify security loopholes. In this process, he started to circumvent the network protection tools and firewalls used in the company. He employed a technique that can create forged TCP sessions by carrying out multiple SYN, ACK, and RST or FIN packets. Further, this process allowed Jude to execute DDoS attacks that can exhaust the network resources.
What is the attack technique used by Jude for finding loopholes in the above scenario?
- UDP flood attack
- Ping-of-death attack
- Spoofed session flood attack
- Peer-to-peer attack
Correct answer: C
Question 2
Jacob works as a system administrator in an organization. He wants to extract the source code of a mobile application and disassemble the application to analyze its design flaws. Using this technique, he wants to fix any bugs in the application, discover underlying vulnerabilities, and improve defense strategies against attacks.
What is the technique used by Jacob in the above scenario to improve the security of the mobile application?
- Reverse engineering
- App sandboxing
- Jailbreaking
- Social engineering
Correct answer: A
Question 3
Which of the following antennas is commonly used in communications for a frequency band of 10 MHz to VHF and UHF?
- Yagi antenna
- Dipole antenna
- Parabolic grid antenna
- Omnidirectional antenna
Correct answer: A
Question 4
Which of the following is the BEST way to defend against network sniffing?
- Using encryption protocols to secure network communications
- Register all machines MAC Address in a Centralized Database
- Use Static IP Address
- Restrict Physical Access to Server Rooms hosting Critical Servers
Correct answer: A
Question 5
Gerard, a disgruntled ex-employee of Sunglass IT Solutions, targets this organization to perform sophisticated attacks and bring down its reputation in the market.
To launch the attacks process, he performed DNS footprinting to gather information about ONS servers and to identify the hosts connected in the target network.
He used an automated tool that can retrieve information about DNS zone data including DNS domain names, computer names. IP addresses. DNS records, and network Who is records. He further exploited this information to launch other sophisticated attacks. What is the tool employed by Gerard in the above scenario?
- Knative
- zANTI
- Towelroot
- Bluto
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
https://www.darknet.org.uk/2017/07/bluto-dns-recon-zone-transfer-brute-forcer/"Attackers also use DNS lookup tools such as DNSdumpster.com, Bluto, and Domain Dossier to retrieve DNS records for a specified domain or hostname. These tools retrieve information such as domains and IP addresses, domain Whois records, DNS records, and network Whois records." CEH Module 02 Page 138 https://www.darknet.org.uk/2017/07/bluto-dns-recon-zone-transfer-brute-forcer/
"Attackers also use DNS lookup tools such as DNSdumpster.com, Bluto, and Domain Dossier to retrieve DNS records for a specified domain or hostname. These tools retrieve information such as domains and IP addresses, domain Whois records, DNS records, and network Whois records." CEH Module 02 Page 138
Question 6
John the Ripper is a technical assessment tool used to test the weakness of which of the following?
- Passwords
- File permissions
- Firewall rulesets
- Usernames
Correct answer: A
Question 7
An attacker has installed a RAT on a host. The attacker wants to ensure that when a user attempts to go to "www.MyPersonalBank.com", the user is directed to a phishing site.
Which file does the attacker need to modify?
- Boot.ini
- Sudoers
- Networks
- Hosts
Correct answer: D
Question 8
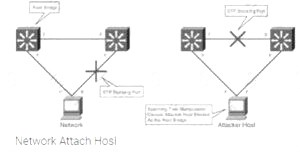
Robin, a professional hacker, targeted an organization's network to sniff all the traffic. During this process. Robin plugged in a rogue switch to an unused port in the LAN with a priority lower than any other switch in the network so that he could make it a root bridge that will later allow him to sniff all the traffic in the network.
What is the attack performed by Robin in the above scenario?
- ARP spoofing attack
- VLAN hopping attack
- DNS poisoning attack
- STP attack
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
STP prevents bridging loops in a redundant switched network environment. By avoiding loops, you can ensure that broadcast traffic does not become a traffic storm. STP is a hierarchical tree-like topology with a “root” switch at the top. A switch is elected as root based on the lowest configured priority of any switch (0 through 65,535). When a switch boots up, it begins a process of identifying other switches and determining the root bridge. After a root bridge is elected, the topology is established from its perspective of the connectivity. The switches determine the path to the root bridge, and all redundant paths are blocked. STP sends configuration and topology change notifications and acknowledgments (TCN/TCA) using bridge protocol data units (BPDU). An STP attack involves an attacker spoofing the root bridge in the topology. The attacker broadcasts out an STP configuration/topology change BPDU in an attempt to force an STP recalculation. The BPDU sent out announces that the attacker’s system has a lower bridge priority. The attacker can then see a variety of frames forwarded from other switches to it. STP recalculation may also cause a denial-of-service (DoS) condition on the network by causing an interruption of 30 to 45 seconds each time the root bridge changes. An attacker using STP network topology changes to force its host to be elected as the root bridge.
switch STP prevents bridging loops in a redundant switched network environment. By avoiding loops, you can ensure that broadcast traffic does not become a traffic storm.
STP is a hierarchical tree-like topology with a “root” switch at the top. A switch is elected as root based on the lowest configured priority of any switch (0 through 65,535). When a switch boots up, it begins a process of identifying other switches and determining the root bridge. After a root bridge is elected, the topology is established from its perspective of the connectivity. The switches determine the path to the root bridge, and all redundant paths are blocked. STP sends configuration and topology change notifications and acknowledgments (TCN/TCA) using bridge protocol data units (BPDU).
An STP attack involves an attacker spoofing the root bridge in the topology. The attacker broadcasts out an STP configuration/topology change BPDU in an attempt to force an STP recalculation. The BPDU sent out announces that the attacker’s system has a lower bridge priority. The attacker can then see a variety of frames forwarded from other switches to it. STP recalculation may also cause a denial-of-service (DoS) condition on the network by causing an interruption of 30 to 45 seconds each time the root bridge changes. An attacker using STP network topology changes to force its host to be elected as the root bridge.

switch
Question 9
Bill is a network administrator. He wants to eliminate unencrypted traffic inside his company's network. He decides to setup a SPAN port and capture all traffic to the datacenter. He immediately discovers unencrypted traffic in port UDP 161. what protocol is this port using and how can he secure that traffic?
- it is not necessary to perform any actions, as SNMP is not carrying important information.
- SNMP and he should change it to SNMP V3
- RPC and the best practice is to disable RPC completely
- SNMP and he should change it to SNMP v2, which is encrypted
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
We have various articles already in our documentation for setting up SNMPv2 trap handling in Opsview, but SNMPv3 traps are a whole new ballgame. They can be quite confusing and complicated to set up the firs time you go through the process, but when you understand what is going on, everything should make more sense. SNMP has gone through several revisions to improve performance and security (version 1, 2c and 3). By default, it is a UDP port based protocol where communication is based on a ‘fire and forget’ methodology in which network packets are sent to another device, but there is no check for receipt of that packet (versus TCP port when a network packet must be acknowledged by the other end of the communication link). There are two modes of operation with SNMP – get requests (or polling) where one device requests information from an SNMP enabled device on a regular basis (normally using UDP port 161), and traps where the SNMP enabled device sends a message to another device when an event occurs (normally using UDP port 162). The latter includes instances such as someone logging on, the device powering up or down, or a wide variety of other problems that would need this type of investigation. This blog covers SNMPv3 traps, as polling and version 2c traps are covered elsewhere in our documentation. SNMP trapsSince SNMP is primarily a UDP port based system, traps may be ‘lost’ when sending between devices; the sending device does not wait to see if the receiver got the trap. This means if the configuration on the sending device is wrong (using the wrong receiver IP address or port) or the receiver isn’t listening for traps or rejecting them out of hand due to misconfiguration, the sender will never know. The SNMP v2c specification introduced the idea of splitting traps into two types; the original ‘hope it gets there’ trap and the newer ‘INFORM’ traps. Upon receipt of an INFORM, the receiver must send an acknowledgement back. If the sender doesn’t get the acknowledgement back, then it knows there is an existing problem and can log it for sysadmins to find when they interrogate the device. We have various articles already in our documentation for setting up SNMPv2 trap handling in Opsview, but SNMPv3 traps are a whole new ballgame. They can be quite confusing and complicated to set up the firs time you go through the process, but when you understand what is going on, everything should make more sense.
SNMP has gone through several revisions to improve performance and security (version 1, 2c and 3). By default, it is a UDP port based protocol where communication is based on a ‘fire and forget’ methodology in which network packets are sent to another device, but there is no check for receipt of that packet (versus TCP port when a network packet must be acknowledged by the other end of the communication link).
There are two modes of operation with SNMP – get requests (or polling) where one device requests information from an SNMP enabled device on a regular basis (normally using UDP port 161), and traps where the SNMP enabled device sends a message to another device when an event occurs (normally using UDP port 162). The latter includes instances such as someone logging on, the device powering up or down, or a wide variety of other problems that would need this type of investigation.
This blog covers SNMPv3 traps, as polling and version 2c traps are covered elsewhere in our documentation. SNMP trapsSince SNMP is primarily a UDP port based system, traps may be ‘lost’ when sending between devices; the sending device does not wait to see if the receiver got the trap. This means if the configuration on the sending device is wrong (using the wrong receiver IP address or port) or the receiver isn’t listening for traps or rejecting them out of hand due to misconfiguration, the sender will never know.
The SNMP v2c specification introduced the idea of splitting traps into two types; the original ‘hope it gets there’ trap and the newer ‘INFORM’ traps. Upon receipt of an INFORM, the receiver must send an acknowledgement back. If the sender doesn’t get the acknowledgement back, then it knows there is an existing problem and can log it for sysadmins to find when they interrogate the device.
Question 10
Mason, a professional hacker, targets an organization and spreads Emotet malware through malicious script. After infecting the victim's device. Mason further used Emotet to spread the infection across local networks and beyond to compromise as many machines as possible. In this process, he used a tool, which is a self-extracting RAR file, to retrieve information related to network resources such as writable share drives.
What is the tool employed by Mason in the above scenario?
- NetPass.exe
- Outlook scraper
- WebBrowserPassView
- Credential enumerator
Correct answer: D

