File Info
| Exam | Certified Ethical Hacker v12 Exam |
| Number | 312-50v12 |
| File Name | ECCouncil.312-50v12.VCEplus.2024-08-20.146q.vcex |
| Size | 2 MB |
| Posted | Aug 20, 2024 |
| Downloads: | 5 |
| Download | ECCouncil.312-50v12.VCEplus.2024-08-20.146q.vcex |
How to open VCEX & EXAM Files?
Files with VCEX & EXAM extensions can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Coupon: MASTEREXAM
With discount: 20%





Demo Questions
Question 1
A friend of yours tells you that he downloaded and executed a file that was sent to him by a coworker. Since the file did nothing when executed, he asks you for help because he suspects that he may have installed a trojan on his computer.
what tests would you perform to determine whether his computer Is Infected?
- Use ExifTool and check for malicious content.
- You do not check; rather, you immediately restore a previous snapshot of the operating system.
- Upload the file to VirusTotal.
- Use netstat and check for outgoing connections to strange IP addresses or domains.
Correct answer: D
Question 2
Garry is a network administrator in an organization. He uses SNMP to manage networked devices from a remote location. To manage nodes in the network, he uses MIB. which contains formal descriptions of all network objects managed by SNMP. He accesses the contents of MIB by using a web browser either by entering the IP address and Lseries.mlb or by entering the DNS library name and Lseries.mlb. He is currently retrieving information from an MIB that contains object types for workstations and server services. Which of the following types of MIB is accessed by Garry in the above scenario?
- LNMIB2.MIB
- WINS.MIB
- DHCP.MIS
- MIB_II.MIB
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
DHCP.MIB: Monitors network traffic between DHCP servers and remote hosts ¦ HOSTMIB.MIB: Monitors and manages host resources ¦ LNMIB2.MIB: Contains object types for workstation and server services ¦ MIBJI.MIB: Manages TCP/IP- based Internet using a simple architecture and system ¦ WINS.MIB: For the Windows Internet Name Service (WINS) DHCP.MIB: Monitors network traffic between DHCP servers and remote hosts ¦ HOSTMIB.MIB: Monitors and manages host resources ¦ LNMIB2.MIB: Contains object types for workstation and server services ¦ MIBJI.MIB: Manages TCP/IP- based Internet using a simple architecture and system ¦ WINS.MIB: For the Windows Internet Name Service (WINS)
Question 3
An attacker redirects the victim to malicious websites by sending them a malicious link by email. The link appears authentic but redirects the victim to a malicious web page, which allows the attacker to steal the victim's data. What type of attack is this?
- Phishing
- Vlishing
- Spoofing
- DDoS
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PhishingPhishing is a type of social engineering attack often used to steal user data, including login credentials and credit card numbers. It occurs when an attacker, masquerading as a trusted entity, dupes a victim into opening an email, instant message, or text message. The recipient is then tricked into clicking a malicious link, which can lead to the installation of malware, the freezing of the system as part of a ransomware attack, or the revealing of sensitive information.An attack can have devastating results. For individuals, this includes unauthorized purchases, the stealing of funds, or identify theft.Moreover, phishing is often used to gain a foothold in corporate or governmental networks as a part of a larger attack, such as an advanced persistent threat (APT) event. In this latter scenario, employees are compromised in order to bypass security perimeters, distribute malware inside a closed environment, or gain privileged access to secured data.An organization succumbing to such an attack typically sustains severe financial losses in addition to declining market share, reputation, and consumer trust. Depending on the scope, a phishing attempt might escalate into a security incident from which a business will have a difficult time recovering.Incorrect answers:Vishing https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voice_phishingVoice phishing, or vishing, is the use of telephony (often Voice over IP telephony) to conduct phishing attacks.DDoS https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Denial-of-service_attackA distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack is a malicious attempt to disrupt the normal traffic of a targeted server, service or network by overwhelming the target or its surrounding infrastructure with a flood of Internet traffic.DDoS attacks achieve effectiveness by utilizing multiple compromised computer systems as sources of attack traffic. Exploited machines can include computers and other networked resources such as IoT devices.Spoofing https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spoofing_attack In the context of information security, and especially network security, a spoofing attack is a situation in which a person or program successfully identifies as another by falsifying data, to gain an illegitimate advantage. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phishing
Phishing is a type of social engineering attack often used to steal user data, including login credentials and credit card numbers. It occurs when an attacker, masquerading as a trusted entity, dupes a victim into opening an email, instant message, or text message. The recipient is then tricked into clicking a malicious link, which can lead to the installation of malware, the freezing of the system as part of a ransomware attack, or the revealing of sensitive information.
An attack can have devastating results. For individuals, this includes unauthorized purchases, the stealing of funds, or identify theft.
Moreover, phishing is often used to gain a foothold in corporate or governmental networks as a part of a larger attack, such as an advanced persistent threat (APT) event. In this latter scenario, employees are compromised in order to bypass security perimeters, distribute malware inside a closed environment, or gain privileged access to secured data.
An organization succumbing to such an attack typically sustains severe financial losses in addition to declining market share, reputation, and consumer trust. Depending on the scope, a phishing attempt might escalate into a security incident from which a business will have a difficult time recovering.
Incorrect answers:
Vishing https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voice_phishing
Voice phishing, or vishing, is the use of telephony (often Voice over IP telephony) to conduct phishing attacks.
DDoS https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Denial-of-service_attack
A distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack is a malicious attempt to disrupt the normal traffic of a targeted server, service or network by overwhelming the target or its surrounding infrastructure with a flood of Internet traffic.
DDoS attacks achieve effectiveness by utilizing multiple compromised computer systems as sources of attack traffic. Exploited machines can include computers and other networked resources such as IoT devices.
Spoofing https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spoofing_attack In the context of information security, and especially network security, a spoofing attack is a situation in which a person or program successfully identifies as another by falsifying data, to gain an illegitimate advantage.
Question 4
Steve, an attacker, created a fake profile on a social media website and sent a request to Stell a. Stella was enthralled by Steve's profile picture and the description given for his profile, and she initiated a conversation with him soon after accepting the request. After a few days. Sieve started asking about her company details and eventually gathered all the essential information regarding her company. What is the social engineering technique Steve employed in the above scenario?
- Diversion theft
- Baiting
- Honey trap
- Piggybacking
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
The honey trap is a technique where an attacker targets a person online by pretending to be an attractive person and then begins a fake online relationship to obtain confidential information about the target company. In this technique, the victim is an insider who possesses critical information about the target organization.Baiting is a technique in which attackers offer end users something alluring in exchange for important information such as login details and other sensitive data. This technique relies on the curiosity and greed of the endusers.Attackers perform this technique by leaving a physical device such as a USB flash drive containing malicious files in locations where people can easily find them, such as parking lots, elevators, and bathrooms. This physical device is labeled with a legitimate company's logo, thereby tricking end-users into trusting it and opening it on their systems. Once the victim connects and opens the device, a malicious file downloads. It infects the system and allows the attacker to take control.For example, an attacker leaves some bait in the form of a USB drive in the elevator with the label "Employee Salary Information 2019" and a legitimate company's logo. Out of curiosity and greed, the victim picks up the device and opens it up on their system, which downloads the bait. Once the bait is downloaded, a piece of malicious software installs on the victim's system, giving the attacker access. The honey trap is a technique where an attacker targets a person online by pretending to be an attractive person and then begins a fake online relationship to obtain confidential information about the target company. In this technique, the victim is an insider who possesses critical information about the target organization.
Baiting is a technique in which attackers offer end users something alluring in exchange for important information such as login details and other sensitive data. This technique relies on the curiosity and greed of the endusers.
Attackers perform this technique by leaving a physical device such as a USB flash drive containing malicious files in locations where people can easily find them, such as parking lots, elevators, and bathrooms. This physical device is labeled with a legitimate company's logo, thereby tricking end-users into trusting it and opening it on their systems. Once the victim connects and opens the device, a malicious file downloads. It infects the system and allows the attacker to take control.
For example, an attacker leaves some bait in the form of a USB drive in the elevator with the label "Employee Salary Information 2019" and a legitimate company's logo. Out of curiosity and greed, the victim picks up the device and opens it up on their system, which downloads the bait. Once the bait is downloaded, a piece of malicious software installs on the victim's system, giving the attacker access.
Question 5
This form of encryption algorithm is asymmetric key block cipher that is characterized by a 128-bit block size, and its key size can be up to 256 bits. Which among the following is this encryption algorithm?
- Twofish encryption algorithm
- HMAC encryption algorithm
- IDEA
- Blowfish encryption algorithm
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
Twofish is an encryption algorithm designed by Bruce Schneier. It's a symmetric key block cipher with a block size of 128 bits, with keys up to 256 bits. it's associated with AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and an earlier block cipher called Blowfish. Twofish was actually a finalist to become the industry standard for encryption, but was ultimately beaten out by the present AES.Twofish has some distinctive features that set it aside from most other cryptographic protocols. For one, it uses pre-computed, key-dependent S-boxes. An S-box (substitution-box) may be a basic component of any symmetric key algorithm which performs substitution. within the context of Twofish's block cipher, the S-box works to obscure the connection of the key to the ciphertext.Twofish uses a pre-computed, key-dependent S-box which suggests that the S-box is already provided, but depends on the cipher key to decrypt the knowledge .How Secure is Twofish?Twofish is seen as a really secure option as far as encryption protocols go. one among the s that it wasn't selected because the advanced encryption standard is thanks to its slower speed. Any encryption standard that uses a 128-bit or higher key, is theoretically safe from brute force attacks.Twofish is during this category.Because Twofish uses "pre-computed key-dependent S-boxes", it are often susceptible to side channel attacks. this is often thanks to the tables being pre-computed. However, making these tables key-dependent helps mitigate that risk.There are a couple of attacks on Twofish, but consistent with its creator, Bruce Schneier, it didn't constitute a real cryptanalysis. These attacks didn't constitue a practical break within the cipher.Products That Use Twofish GnuPG: GnuPG may be a complete and free implementation of the OpenPGP standard as defined by RFC4880 (also referred to as PGP). GnuPG allows you to encrypt and sign your data and communications; it features a flexible key management system, along side access modules for all types of public key directories.KeePass: KeePass may be a password management tool that generates passwords with top-notch security. It's a free, open source, lightweight and easy-to-use password manager with many extensions and plugins.Password Safe: Password Safe uses one master password to stay all of your passwords protected, almost like the functionality of most of the password managers on this list. It allows you to store all of your passwords during a single password database, or multiple databases for various purposes.Creating a database is straightforward , just create the database, set your master password.PGP (Pretty Good Privacy): PGP is employed mostly for email encryption, it encrypts the content of the e-mail . However, Pretty Good Privacy doesn't encrypt the topic and sender of the e-mail , so make certain to never put sensitive information in these fields when using PGP.TrueCrypt: TrueCrypt may be a software program that encrypts and protects files on your devices.With TrueCrypt the encryption is transparent to the user and is completed locally at the user's computer. this suggests you'll store a TrueCrypt file on a server and TrueCrypt will encrypt that file before it's sent over the network. Twofish is an encryption algorithm designed by Bruce Schneier. It's a symmetric key block cipher with a block size of 128 bits, with keys up to 256 bits. it's associated with AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and an earlier block cipher called Blowfish. Twofish was actually a finalist to become the industry standard for encryption, but was ultimately beaten out by the present AES.
Twofish has some distinctive features that set it aside from most other cryptographic protocols. For one, it uses pre-computed, key-dependent S-boxes. An S-box (substitution-box) may be a basic component of any symmetric key algorithm which performs substitution. within the context of Twofish's block cipher, the S-box works to obscure the connection of the key to the ciphertext.
Twofish uses a pre-computed, key-dependent S-box which suggests that the S-box is already provided, but depends on the cipher key to decrypt the knowledge .
How Secure is Twofish?
Twofish is seen as a really secure option as far as encryption protocols go. one among the s that it wasn't selected because the advanced encryption standard is thanks to its slower speed. Any encryption standard that uses a 128-bit or higher key, is theoretically safe from brute force attacks.
Twofish is during this category.
Because Twofish uses "pre-computed key-dependent S-boxes", it are often susceptible to side channel attacks. this is often thanks to the tables being pre-computed. However, making these tables key-dependent helps mitigate that risk.
There are a couple of attacks on Twofish, but consistent with its creator, Bruce Schneier, it didn't constitute a real cryptanalysis. These attacks didn't constitue a practical break within the cipher.
Products That Use Twofish GnuPG: GnuPG may be a complete and free implementation of the OpenPGP standard as defined by RFC4880 (also referred to as PGP). GnuPG allows you to encrypt and sign your data and communications; it features a flexible key management system, along side access modules for all types of public key directories.
KeePass: KeePass may be a password management tool that generates passwords with top-notch security. It's a free, open source, lightweight and easy-to-use password manager with many extensions and plugins.
Password Safe: Password Safe uses one master password to stay all of your passwords protected, almost like the functionality of most of the password managers on this list. It allows you to store all of your passwords during a single password database, or multiple databases for various purposes.
Creating a database is straightforward , just create the database, set your master password.
PGP (Pretty Good Privacy): PGP is employed mostly for email encryption, it encrypts the content of the e-mail . However, Pretty Good Privacy doesn't encrypt the topic and sender of the e-mail , so make certain to never put sensitive information in these fields when using PGP.
TrueCrypt: TrueCrypt may be a software program that encrypts and protects files on your devices.
With TrueCrypt the encryption is transparent to the user and is completed locally at the user's computer. this suggests you'll store a TrueCrypt file on a server and TrueCrypt will encrypt that file before it's sent over the network.
Question 6
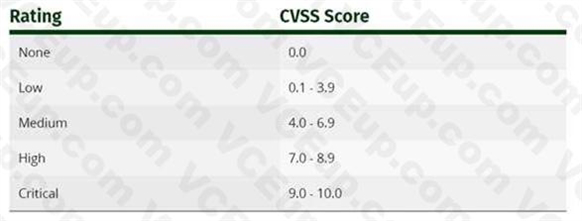
Sam is working as a system administrator In an organization. He captured the principal characteristics of a vulnerability and produced a numerical score to reflect Its severity using CVSS v3.0 to property assess and prioritize the organization's vulnerability management processes. The base score that Sam obtained after performing cvss rating was 4.0. What is the CVSS severity level of the vulnerability discovered by Sam in the above scenario?
- Medium
- Low
- Critical
- High
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
Rating CVSS ScoreNone 0.0Low 0.1 - 3.9Medium 4.0 - 6.9High 7.0 - 8.9Critical 9.0 - 10.0https://www.first.org/cvss/v3.0/specification-document The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is an open framework for communicating the characteristics and severity of software vulnerabilities. CVSS consists of three metric groups: Base, Temporal, and Environmental. The Base metrics produce a score ranging from 0 to 10, which can then be modified by scoring the Temporal and Environmental metrics. A CVSS score is also represented as a vector string, a compressed textual representation of the values used to derive the score. Thus, CVSS is well suited as a standard measurement system for industries, organizations, and governments that need accurate and consistent vulnerability severity scores. Two common uses of CVSS are calculating the severity of vulnerabilities discovered on one's systems and as a factor in prioritization of vulnerability remediation activities. The National Vulnerability Database (NVD) provides CVSS scores for almost all known vulnerabilities.Qualitative Severity Rating ScaleFor some purposes, it is useful to have a textual representation of the numeric Base, Temporal and Environmental scores. Rating CVSS Score
None 0.0
Low 0.1 - 3.9
Medium 4.0 - 6.9
High 7.0 - 8.9
Critical 9.0 - 10.0
https://www.first.org/cvss/v3.0/specification-document The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is an open framework for communicating the characteristics and severity of software vulnerabilities. CVSS consists of three metric groups: Base, Temporal, and Environmental. The Base metrics produce a score ranging from 0 to 10, which can then be modified by scoring the Temporal and Environmental metrics. A CVSS score is also represented as a vector string, a compressed textual representation of the values used to derive the score. Thus, CVSS is well suited as a standard measurement system for industries, organizations, and governments that need accurate and consistent vulnerability severity scores. Two common uses of CVSS are calculating the severity of vulnerabilities discovered on one's systems and as a factor in prioritization of vulnerability remediation activities. The National Vulnerability Database (NVD) provides CVSS scores for almost all known vulnerabilities.
Qualitative Severity Rating Scale
For some purposes, it is useful to have a textual representation of the numeric Base, Temporal and Environmental scores.

Question 7
jane invites her friends Alice and John over for a LAN party. Alice and John access Jane's wireless network without a password. However. Jane has a long, complex password on her router. What attack has likely occurred?
- Wireless sniffing
- Piggybacking
- Evil twin
- Wardriving
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
An evil twin may be a fraudulent Wi-Fi access point that appears to be legitimate but is about up to pay attention to wireless communications.[1] The evil twin is that the wireless LAN equivalent of the phishing scam.This type of attack could also be wont to steal the passwords of unsuspecting users, either by monitoring their connections or by phishing, which involves fixing a fraudulent internet site and luring people there.The attacker snoops on Internet traffic employing a bogus wireless access point. Unwitting web users could also be invited to log into the attacker's server, prompting them to enter sensitive information like usernames and passwords. Often, users are unaware they need been duped until well after the incident has occurred.When users log into unsecured (non-HTTPS) bank or e-mail accounts, the attacker intercepts thetransaction, since it's sent through their equipment. The attacker is additionally ready to hook upwith other networks related to the users' credentials.Fake access points are found out by configuring a wireless card to act as an access point (known as HostAP). they're hard to trace since they will be shut off instantly. The counterfeit access point could also be given an equivalent SSID and BSSID as a close-by Wi-Fi network. The evil twin are often configured to pass Internet traffic through to the legitimate access point while monitoring the victim's connection, or it can simply say the system is temporarily unavailable after obtaining a username and password. An evil twin may be a fraudulent Wi-Fi access point that appears to be legitimate but is about up to pay attention to wireless communications.[1] The evil twin is that the wireless LAN equivalent of the phishing scam.
This type of attack could also be wont to steal the passwords of unsuspecting users, either by monitoring their connections or by phishing, which involves fixing a fraudulent internet site and luring people there.
The attacker snoops on Internet traffic employing a bogus wireless access point. Unwitting web users could also be invited to log into the attacker's server, prompting them to enter sensitive information like usernames and passwords. Often, users are unaware they need been duped until well after the incident has occurred.
When users log into unsecured (non-HTTPS) bank or e-mail accounts, the attacker intercepts thetransaction, since it's sent through their equipment. The attacker is additionally ready to hook upwith other networks related to the users' credentials.
Fake access points are found out by configuring a wireless card to act as an access point (known as HostAP). they're hard to trace since they will be shut off instantly. The counterfeit access point could also be given an equivalent SSID and BSSID as a close-by Wi-Fi network. The evil twin are often configured to pass Internet traffic through to the legitimate access point while monitoring the victim's connection, or it can simply say the system is temporarily unavailable after obtaining a username and password.
Question 8
Nicolas just found a vulnerability on a public-facing system that is considered a zero-day vulnerability.
He sent an email to the owner of the public system describing the problem and how the owner can protect themselves from that vulnerability. He also sent an email to Microsoft informing them of the problem that their systems are exposed to. What type of hacker is Nicolas?
- Red hat
- white hat
- Black hat
- Gray hat
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
A white hat (or a white hat hacker) is an ethical computer hacker, or a computer security expert, who focuses on penetration testing and in other testing methodologies that ensures the safety of an organization's information systems. Ethical hacking may be a term meant to imply a broader category than simply penetration testing. Contrasted with black hat, a malicious hacker, the name comes from Western films, where heroic and antagonistic cowboys might traditionally wear a white and a black hat respectively. While a white hat hacker hacks under good intentions with permission, and a black hat hacker, most frequently unauthorized, has malicious intent, there's a 3rd kind referred to as a gray hat hacker who hacks with good intentions but sometimes without permission.White hat hackers can also add teams called "sneakers and/or hacker clubs",red teams, or tiger teams.While penetration testing concentrates on attacking software and computer systems from the beginning – scanning ports, examining known defects in protocols and applications running on the system and patch installations, as an example – ethical hacking may include other things. A fullblown ethical hack might include emailing staff to invite password details, searching through executive's dustbins and typically breaking and entering, without the knowledge and consent of the targets. Only the owners, CEOs and Board Members (stake holders) who asked for such a censoring of this magnitude are aware. to undertake to duplicate a number of the destructive techniques a true attack might employ, ethical hackers may arrange for cloned test systems, or organize a hack late in the dark while systems are less critical. In most up-to-date cases these hacks perpetuate for the longterm con (days, if not weeks, of long-term human infiltration into an organization). Some examples include leaving USB/flash key drives with hidden auto-start software during a public area as if someone lost the tiny drive and an unsuspecting employee found it and took it.Some other methods of completing these include: DoS attacks Social engineering tactics Reverse engineering Network security Disk and memory forensics Vulnerability research Security scanners such as:– W3af– Nessus– Burp suite Frameworks such as:– Metasploit Training PlatformsThese methods identify and exploit known security vulnerabilities and plan to evade security to realize entry into secured areas. they're ready to do that by hiding software and system 'back-doors' which will be used as a linkto information or access that a non-ethical hacker, also referred to as 'black-hat' or 'grey-hat', might want to succeed in . A white hat (or a white hat hacker) is an ethical computer hacker, or a computer security expert, who focuses on penetration testing and in other testing methodologies that ensures the safety of an organization's information systems. Ethical hacking may be a term meant to imply a broader category than simply penetration testing. Contrasted with black hat, a malicious hacker, the name comes from Western films, where heroic and antagonistic cowboys might traditionally wear a white and a black hat respectively. While a white hat hacker hacks under good intentions with permission, and a black hat hacker, most frequently unauthorized, has malicious intent, there's a 3rd kind referred to as a gray hat hacker who hacks with good intentions but sometimes without permission.
White hat hackers can also add teams called "sneakers and/or hacker clubs",red teams, or tiger teams.
While penetration testing concentrates on attacking software and computer systems from the beginning – scanning ports, examining known defects in protocols and applications running on the system and patch installations, as an example – ethical hacking may include other things. A fullblown ethical hack might include emailing staff to invite password details, searching through executive's dustbins and typically breaking and entering, without the knowledge and consent of the targets. Only the owners, CEOs and Board Members (stake holders) who asked for such a censoring of this magnitude are aware. to undertake to duplicate a number of the destructive techniques a true attack might employ, ethical hackers may arrange for cloned test systems, or organize a hack late in the dark while systems are less critical. In most up-to-date cases these hacks perpetuate for the longterm con (days, if not weeks, of long-term human infiltration into an organization). Some examples include leaving USB/flash key drives with hidden auto-start software during a public area as if someone lost the tiny drive and an unsuspecting employee found it and took it.
Some other methods of completing these include:
DoS attacks
Social engineering tactics
Reverse engineering
Network security
Disk and memory forensics
Vulnerability research
Security scanners such as:
– W3af
– Nessus
– Burp suite
Frameworks such as:
– Metasploit
Training Platforms
These methods identify and exploit known security vulnerabilities and plan to evade security to realize entry into secured areas. they're ready to do that by hiding software and system 'back-doors' which will be used as a link
to information or access that a non-ethical hacker, also referred to as 'black-hat' or 'grey-hat', might want to succeed in .
Question 9
You are a penetration tester tasked with testing the wireless network of your client Brakeme SA. You are attempting to break into the wireless network with the SSID `Brakeme-Internal.` You realize that this network uses WPA3 encryption.
Which of the following vulnerabilities is the promising to exploit?
- Dragonblood
- Cross-site request forgery
- Key reinstallation attack
- AP Myconfiguration
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
Dragonblood allows an attacker in range of a password-protected Wi-Fi network to get the password and gain access to sensitive information like user credentials, emails and mastercard numbers. consistent with the published report:"The WPA3 certification aims to secure Wi-Fi networks, and provides several advantages over its predecessor WPA2, like protection against offline dictionary attacks and forward secrecy.Unfortunately, we show that WPA3 is suffering from several design flaws, and analyze these flaws both theoretically and practically. Most prominently, we show that WPA3's Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE) handshake, commonly referred to as Dragonfly, is suffering from password partitioning attacks." Our Wi-Fi researchers at WatchGuard are educating businesses globally that WPA3 alone won't stop the Wi-Fi hacks that allow attackers to steal information over the air (learn more in our recent blog post on the topic). These Dragonblood vulnerabilities impact alittle amount of devices that were released with WPA3 support, and makers are currently making patches available. one among the most important takeaways for businesses of all sizes is to know that a long-term fix might not be technically feasible for devices with lightweight processing capabilities like IoT and embedded systems. Businesses got to consider adding products that enable a Trusted Wireless Environment for all kinds of devices and users alike.Recognizing that vulnerabilities like KRACK and Dragonblood require attackers to initiate these attacks by bringing an "Evil Twin" Access Point or a Rogue Access Point into a Wi-Fi environment, we've been that specialize in developing Wi- Fi security solutions that neutralize these threats in order that these attacks can never occur. The Trusted Wireless Environment framework protects against the "Evil Twin" Access Point and Rogue Access Point.one among these hacks is required to initiate the 2 downgrade or side-channel attacks referenced in Dragonblood.What's next? WPA3 is an improvement over WPA2 Wi-Fi encryption protocol, however, as we predicted, it still doesn't provide protection from the six known Wi-Fi threat categories. It's highly likely that we'll see more WPA3 vulnerabilities announced within the near future.To help reduce Wi-Fi vulnerabilities, we're asking all of you to hitch the Trusted Wireless Environment movement and advocate for a worldwide security standard for Wi-Fi. Dragonblood allows an attacker in range of a password-protected Wi-Fi network to get the password and gain access to sensitive information like user credentials, emails and mastercard numbers. consistent with the published report:
"The WPA3 certification aims to secure Wi-Fi networks, and provides several advantages over its predecessor WPA2, like protection against offline dictionary attacks and forward secrecy.
Unfortunately, we show that WPA3 is suffering from several design flaws, and analyze these flaws both theoretically and practically. Most prominently, we show that WPA3's Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE) handshake, commonly referred to as Dragonfly, is suffering from password partitioning attacks." Our Wi-Fi researchers at WatchGuard are educating businesses globally that WPA3 alone won't stop the Wi-Fi hacks that allow attackers to steal information over the air (learn more in our recent blog post on the topic). These Dragonblood vulnerabilities impact alittle amount of devices that were released with WPA3 support, and makers are currently making patches available. one among the most important takeaways for businesses of all sizes is to know that a long-term fix might not be technically feasible for devices with lightweight processing capabilities like IoT and embedded systems. Businesses got to consider adding products that enable a Trusted Wireless Environment for all kinds of devices and users alike.
Recognizing that vulnerabilities like KRACK and Dragonblood require attackers to initiate these attacks by bringing an "Evil Twin" Access Point or a Rogue Access Point into a Wi-Fi environment, we've been that specialize in developing Wi- Fi security solutions that neutralize these threats in order that these attacks can never occur. The Trusted Wireless Environment framework protects against the "Evil Twin" Access Point and Rogue Access Point.
one among these hacks is required to initiate the 2 downgrade or side-channel attacks referenced in Dragonblood.
What's next? WPA3 is an improvement over WPA2 Wi-Fi encryption protocol, however, as we predicted, it still doesn't provide protection from the six known Wi-Fi threat categories. It's highly likely that we'll see more WPA3 vulnerabilities announced within the near future.
To help reduce Wi-Fi vulnerabilities, we're asking all of you to hitch the Trusted Wireless Environment movement and advocate for a worldwide security standard for Wi-Fi.
Question 10
To invisibly maintain access to a machine, an attacker utilizes a toolkit that sits undetected In the core components of the operating system. What is this type of rootkit an example of?
- Mypervisor rootkit
- Kernel toolkit
- Hardware rootkit
- Firmware rootkit
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
Kernel-mode rootkits run with the best operating system privileges (Ring 0) by adding code or replacement parts of the core operating system, as well as each the kernel and associated device drivers. Most operative systems support kernel- mode device drivers, that execute with a similar privileges because the software itself. As such, several kernel-mode rootkits square measure developed as device drivers or loadable modules, like loadable kernel modules in Linux or device drivers in Microsoft Windows. This category of rootkit has unrestricted security access, however is tougher to jot down. The quality makes bugs common, and any bugs in code operative at the kernel level could seriously impact system stability, resulting in discovery of the rootkit. one amongst the primary wide familiar kernel rootkits was developed for Windows NT four.0 and discharged in Phrack magazine in 1999 by Greg Hoglund. Kernel rootkits is particularly tough to observe and take away as a result of they operate at a similar security level because the software itself, and square measure therefore able to intercept or subvert the foremost sure software operations. Any package, like antivirus package, running on the compromised system is equally vulnerable. during this scenario, no a part of the system is sure. Kernel-mode rootkits run with the best operating system privileges (Ring 0) by adding code or replacement parts of the core operating system, as well as each the kernel and associated device drivers. Most operative systems support kernel- mode device drivers, that execute with a similar privileges because the software itself. As such, several kernel-mode rootkits square measure developed as device drivers or loadable modules, like loadable kernel modules in Linux or device drivers in Microsoft Windows. This category of rootkit has unrestricted security access, however is tougher to jot down. The quality makes bugs common, and any bugs in code operative at the kernel level could seriously impact system stability, resulting in discovery of the rootkit. one amongst the primary wide familiar kernel rootkits was developed for Windows NT four.0 and discharged in Phrack magazine in 1999 by Greg Hoglund. Kernel rootkits is particularly tough to observe and take away as a result of they operate at a similar security level because the software itself, and square measure therefore able to intercept or subvert the foremost sure software operations. Any package, like antivirus package, running on the compromised system is equally vulnerable. during this scenario, no a part of the system is sure.

