File Info
| Exam | IBM AIX v7 Administrator Specialty |
| Number | S1000-007 |
| File Name | IBM.S1000-007.CertDumps.2023-07-11.46q.vcex |
| Size | 624 KB |
| Posted | Jul 11, 2023 |
| Download | IBM.S1000-007.CertDumps.2023-07-11.46q.vcex |
How to open VCEX & EXAM Files?
Files with VCEX & EXAM extensions can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Coupon: MASTEREXAM
With discount: 20%





Demo Questions
Question 1
What are three states a device can have when connected to an AIX system?
- Available
- Defined
- Stopped
- Blocked
- Running
- Suspended
Correct answer: ABC
Explanation:
Devices that are connected to the system can be in one of four states. Devices that are connected to the system can be in one of the following states: Item Description Undefined The device is unknown to the system. Defined Specific information about the device is recorded in the customized database, but it is unavailable to the system. Available A defined device is coupled to the operating system, or the defined device is configured. Stopped The device is unavailable but remains known by its device driver. If a tty device and a printer alternately use the same tty connector, both a tty device and a printer are defined on the same parent and port in the device configuration database. Only one of these devices can be configured at a time. When the tty connector is configured, the printer specific setup information is retained until it is configured again. The device is not removed; it is in the defined state. Maintaining a device in defined state retains customized information for a device that is not currently in use, either before it is first made available or while it is temporarily removed from the system. If a device driver exists for a device, the device can be made available through the device driver. https://www.ibm.com/docs/en/aix/7.2?topic=nodes-device-states Devices that are connected to the system can be in one of four states.
Devices that are connected to the system can be in one of the following states:
Item Description
Undefined The device is unknown to the system.
Defined Specific information about the device is recorded in the customized database, but it is unavailable to the system.
Available A defined device is coupled to the operating system, or the defined device is configured.
Stopped The device is unavailable but remains known by its device driver.
If a tty device and a printer alternately use the same tty connector, both a tty device and a printer are defined on the same parent and port in the device configuration database. Only one of these devices can be configured at a time.
When the tty connector is configured, the printer specific setup information is retained until it is configured again. The device is not removed; it is in the defined state. Maintaining a device in defined state retains customized information for a device that is not currently in use, either before it is first made available or while it is temporarily removed from the system.
If a device driver exists for a device, the device can be made available through the device driver.
https://www.ibm.com/docs/en/aix/7.2?topic=nodes-device-states
Question 2
What command is used to monitor SAN I/O performance/throughput?
- iostat -DIRT 60 10
- mpstat -w 1
- ioo -L
- vmstat -i 1
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
The command used to monitor SAN I/O performance/throughput is iostat -DIRT 60 10. The iostat command is used to monitor I/O performance and throughput on a SAN device. The DIRT (Disk I/O Response Time) flag can be used to display the response time for each I/O request. The last two arguments, 60 and 10, are the interval (in seconds) and the number of iterations respectively. This command will monitor I/O performance/throughput every 60 seconds for 10 iterations. The command used to monitor SAN I/O performance/throughput is iostat -DIRT 60 10. The iostat command is used to monitor I/O performance and throughput on a SAN device. The DIRT (Disk I/O Response Time) flag can be used to display the response time for each I/O request. The last two arguments, 60 and 10, are the interval (in seconds) and the number of iterations respectively. This command will monitor I/O performance/throughput every 60 seconds for 10 iterations.
Question 3
An IT security department would like to limit root user access to only members of the group called system. Which command will accomplish this?
- chgroup admin=root system
- cruiser sugroups=system root
- chadmin user=root system
- chadmin group=system root
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
The "chadmin" command can be used to modify the attributes of a user account, including the groups that the user belongs to. The syntax for limiting root user access to members of the group called "system" would be: sql chadmin group=system root This command will add the root user to the "system" group and remove it from any other groups. Members of the "system" group will be the only ones able to access the root account. The "chadmin" command can be used to modify the attributes of a user account, including the groups that the user belongs to. The syntax for limiting root user access to members of the group called "system" would be: sql chadmin group=system root This command will add the root user to the "system" group and remove it from any other groups.
Members of the "system" group will be the only ones able to access the root account.
Question 4
Which statement is true regarding the snap command?
- It collects performance related data.
- By default, it will check there is enough space where the data is to be stored.
- C. All options are enabled by default.
- The data must be stored in /tmp.
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
"The command to limit root user access to only members of the group called system is chadmin group=system root. This command will set the primary group of the root user to the system group, thereby limiting root user access to only members of that group. This command can be used to set any user's primary group, not just root." The source of this information is the IBM AIX v7 Administrator Specialty Study Guide. "The command to limit root user access to only members of the group called system is chadmin group=system root. This command will set the primary group of the root user to the system group, thereby limiting root user access to only members of that group. This command can be used to set any user's primary group, not just root." The source of this information is the IBM AIX v7 Administrator Specialty Study Guide.
Question 5
An AIX administrator installed the fileset named useful_fileset. How can they determine which files are included in the fileset?
- file -f useful__fileset
- lslpp -f useful_fileset
- rpm -qf useful_fileset
- lppchk -f useful fileset
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
The "lslpp" command can be used to display information about filesets installed on an AIX system. To determine which files are included in the "useful_fileset" fileset, the administrator can run the following command: lslpp -f useful_fileset This command will display detailed information about the "useful_fileset" fileset, including a list of the files that are included in the fileset. This information can be useful for verifying the installation of the fileset and for troubleshooting problems that may be related to the fileset. The "lslpp" command can be used to display information about filesets installed on an AIX system. To determine which files are included in the "useful_fileset" fileset, the administrator can run the following command: lslpp -f useful_fileset This command will display detailed information about the "useful_fileset" fileset, including a list of the files that are included in the fileset. This information can be useful for verifying the installation of the fileset and for troubleshooting problems that may be related to the fileset.
Question 6
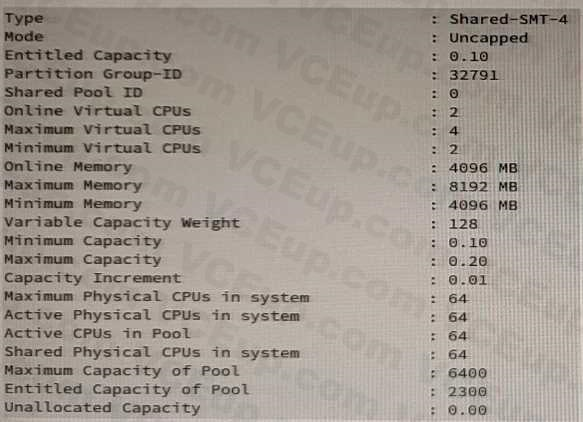
Based on the output from the lparstat command, how many logical processors are configured in the partition?

- 8
- 4
- 64
- 128
Correct answer: D
Question 7
Which command lists filesets that are below AIX V7.2 technology level 4?
- oslevel -r -1 7200-04
- lslpp -s -1 7200-04
- lppchk: -L -F "fileset level" I grep -v "7200-04"
- instfix -i I grep -v 7200-04
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
This command will list all filesets that are below the AIX V7.2 technology level 4. The oslevel command is a useful tool for AIX administrators, as it allows them to list the installed technology levels and filesets. Other commands such as lslpp, lppchk, and instfix are not applicable to this task and will not provide the desired information. For more information on the oslevel command, please refer to the IBM AIX v7 Administrator Specialty Study Guide, page 12-15. The guide can be found here: https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/en/ssw_aix_72/os_upgrade/oslevel_command.htm. This command will list all filesets that are below the AIX V7.2 technology level 4. The oslevel command is a useful tool for AIX administrators, as it allows them to list the installed technology levels and filesets. Other commands such as lslpp, lppchk, and instfix are not applicable to this task and will not provide the desired information.
For more information on the oslevel command, please refer to the IBM AIX v7 Administrator Specialty Study Guide, page 12-15. The guide can be found here:
https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/en/ssw_aix_72/os_upgrade/oslevel_command.htm.
Question 8
A system administrator has noticed that static routes are missing after rebooting a system. What is the most likely reason for this?
- The administrator has failed to configure the routes in the lo0 device with the chdev command.
- The administrator has failed to configure the routes with the route add command.
- The administrator has failed to run the cfgmgr command before rebooting the systems.
- The administrator has failed to configure the routes in the inet0 device with the chdev command.
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
The administrator has failed to run the cfgmgr command before rebooting the systems. Running the cfgmgr command before rebooting a system is important, as it ensures that any changes made to the configuration are written to the system, otherwise the changes may be lost when the system is rebooted. Other commands such as chdev and route add are not related to this issue and will not solve the problem. For more information on the cfgmgr command, please refer to the IBM AIX v7 Administrator Specialty Study Guide, page 10-7. The guide can be found here: https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/en/ssw_aix_72/cfgmgmt/cfgmgr_command.htm. The administrator has failed to run the cfgmgr command before rebooting the systems. Running the cfgmgr command before rebooting a system is important, as it ensures that any changes made to the configuration are written to the system, otherwise the changes may be lost when the system is rebooted. Other commands such as chdev and route add are not related to this issue and will not solve the problem.
For more information on the cfgmgr command, please refer to the IBM AIX v7 Administrator Specialty Study Guide, page 10-7. The guide can be found here:
https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/en/ssw_aix_72/cfgmgmt/cfgmgr_command.htm.
Question 9
Which user account is always UID 0 on AIX?
- bin
- root
- admin
- system
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
The root account is the special user in the /etc/passwd file with the user ID (UID) of 0 and is commonly given the user name, root. It is not the user name that makes the root account so special, but the UID value of 0. This means that any user that has a UID of 0 also has the same privileges as the root user. Also, the root account is always authenticated by means of the local security files. https://www.ibm.com/docs/en/aix/7.2?topic=passwords-root-account The root account is the special user in the /etc/passwd file with the user ID (UID) of 0 and is commonly given the user name, root. It is not the user name that makes the root account so special, but the UID value of 0. This means that any user that has a UID of 0 also has the same privileges as the root user. Also, the root account is always authenticated by means of the local security files.
https://www.ibm.com/docs/en/aix/7.2?topic=passwords-root-account
Question 10
While a system administrator is checking the TCP/IP connectivity between two systems with the traceroute command, the administrator found Fragmentation required messages in the traceroute output.
What is the likely reason for these messages?
- The TCP buffers in the router gateway are exhausted. The source and target system are having TCP/IP communication problems.
- Same MTU sizes between the source and target systems. The source and target systems are using Jumbo Frames. The LPARs are using the same Virtual Switch (vSwitch) Network.
- Different MTU sizes between the source and target systems. The source system is using Jumbo Frames and the target is using the default MTU size.
- The TCP buffers between the source and the target systems are exhausted. The source and target systems are using virtual ethernet adapters.
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
The source system is using Jumbo Frames and the target is using the default MTU size. Fragmentation required messages can appear in traceroute output when the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) size of the source and target systems are different. In this case, the source system is using a larger MTU size (Jumbo Frames) than the target system (default MTU size). As a result, the router gateway must fragment the data packets in order for them to reach their destination. This is why the fragmentation required messages appear in the traceroute output. Reference: IBM AIX v7 Administrator Specialty Study Guide. The source system is using Jumbo Frames and the target is using the default MTU size.
Fragmentation required messages can appear in traceroute output when the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) size of the source and target systems are different. In this case, the source system is using a larger MTU size (Jumbo Frames) than the target system (default MTU size). As a result, the router gateway must fragment the data packets in order for them to reach their destination. This is why the fragmentation required messages appear in the traceroute output. Reference: IBM AIX v7 Administrator Specialty Study Guide.


