File Info
| Exam | Installing and Configuring Windows Server 2012 |
| Number | 70-410 |
| File Name | Microsoft.70-410.Train4Sure.2018-06-14.303q.tqb |
| Size | 12 MB |
| Posted | Jun 14, 2018 |
| Download | Microsoft.70-410.Train4Sure.2018-06-14.303q.tqb |
How to open VCEX & EXAM Files?
Files with VCEX & EXAM extensions can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Coupon: MASTEREXAM
With discount: 20%





Demo Questions
Question 1
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named adatum.com. The domain contains several thousand member servers that run Windows Server 2012 R2. All of the computer accounts for the member servers are in an organizational unit (OU) named ServersAccounts.
Servers are restarted only occasionally.
You need to identify which servers were restarted during the last two days.
What should you do?
- Run dsquery computer and specify the –staiepwd parameter.
- Run Get-ADComputer and specify the SearchScope parameter.
- Run Get-ADComputer and specify the IastLogon property.
- Run dsquery server and specify the –o parameter
Correct answer: C
Question 2
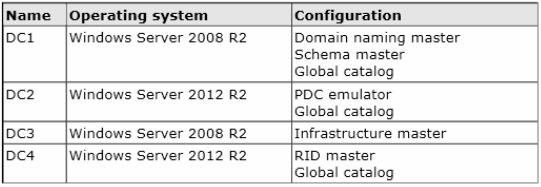
Your network contains an Active Directory forest. The forest contains a single domain named contoso.com. The domain contains four domain controllers. The domain controllers are configured as shown in the following table.

All domain controllers are DNS servers.
You plan to deploy a new domain controller named DC5 in the contoso.com domain.
You need to identify which domain controller must be online to ensure that DC5 can be promoted successfully to a domain controller.
Which domain controller should you identify?
- DC1
- DC2
- DC3
- DC4
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
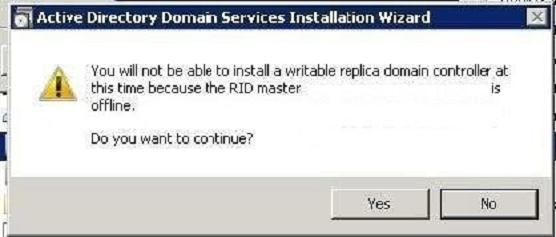
Relative ID (RID) Master:Allocates active and standby RID pools to replica domain controllers in the same domain. (corp.contoso.com). Must be online for newly promoted domain controllers to obtain a local RID pool that is required to advertise or when existing domain controllers have to update their current or standby RID pool allocation. The RID master is responsible for processing RID pool requests from all domain controllers in a particular domain. When a DC creates a security principal object such as a user or group, it attaches a unique Security ID (SID) to the object. This SID consists of a domain SID (the same for all SIDs created in a domain), and a relative ID (RID) that is unique for each security principal SID created in a domain. Each DC in a domain is allocated a pool of RIDs that it is allowed to assign to the security principals it creates. When a DC’s allocated RID pool falls below a threshold, that DC issues a request for additional RIDs to the domain’s RID master. The domain RID master responds to the request by retrieving RIDs from the domain’s unallocated RID pool and assigns them to the pool of the requesting DC At any one time, there can be only one domain controller acting as the RID master in the domain. The Infrastructure Master – The purpose of this role is to ensure that cross-domain object references are correctly handled. For example, if you add a user from one domain to a security group from a different domain, the Infrastructure Master makes sure this is done properly. As you can guess however, if your Active Directory deployment has only a single domain, then the Infrastructure Master role does no work at all, and even in a multi-domain environment it is rarely used except when complex user administration tasks are performed, so the machine holding this role doesn’t need to have much horsepower at all. Relative ID (RID) Master:
Allocates active and standby RID pools to replica domain controllers in the same domain. (corp.contoso.com).
Must be online for newly promoted domain controllers to obtain a local RID pool that is required to advertise or when existing domain controllers have to update their current or standby RID pool allocation.
The RID master is responsible for processing RID pool requests from all domain controllers in a particular domain. When a DC creates a security principal object such as a user or group, it attaches a unique Security ID (SID) to the object. This SID consists of a domain SID (the same for all SIDs created in a domain), and a relative ID (RID) that is unique for each security principal SID created in a domain. Each DC in a domain is allocated a pool of RIDs that it is allowed to assign to the security principals it creates. When a DC’s allocated RID pool falls below a threshold, that DC issues a request for additional RIDs to the domain’s RID master. The domain RID master responds to the request by retrieving RIDs from the domain’s unallocated RID pool and assigns them to the pool of the requesting DC At any one time, there can be only one domain controller acting as the RID master in the domain.

The Infrastructure Master – The purpose of this role is to ensure that cross-domain object references are correctly handled. For example, if you add a user from one domain to a security group from a different domain, the Infrastructure Master makes sure this is done properly. As you can guess however, if your Active Directory deployment has only a single domain, then the Infrastructure Master role does no work at all, and even in a multi-domain environment it is rarely used except when complex user administration tasks are performed, so the machine holding this role doesn’t need to have much horsepower at all.
Question 3
Your network contains an Active Directory forest that contains three domains.
A group named Group1 is configured as a domain local distribution group in the forest root domain.
You plan to grant Group1 read-only access to a shared folder named Share1.Share1 is located in a child domain.
You need to ensure that the members of Group1 can access Share1.
What should you do first?
- Convert Group1 to a universal security group.
- Convert Group1 to a global distribution group.
- Convert Group1 to a universal distribution group.
- Convert Group1 to a domain local security group.
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
Universal can be used for any domain or forest. Furthermore a Universal group can span multiple domains, even the entire forest. References:Exam Ref 70-410: Installing and Configuring Windows Server 2012 R2: Chapter 5: Install and Administer Active Directory, Objective 5.3 Create and manage Active Directory groups and Organization units, p. 289-291, 293http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc781446(v=ws.10).aspxhttp://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc755692(v=ws.10).aspx Universal can be used for any domain or forest. Furthermore a Universal group can span multiple domains, even the entire forest.
References:
Exam Ref 70-410: Installing and Configuring Windows Server 2012 R2: Chapter 5: Install and Administer Active Directory, Objective 5.3 Create and manage Active Directory groups and Organization units, p. 289-291, 293
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc781446(v=ws.10).aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc755692(v=ws.10).aspx

