File Info
| Exam | Developing SQL Databases |
| Number | 70-762 |
| File Name | Microsoft.70-762.SelfTestEngine.2019-04-16.78q.vcex |
| Size | 4 MB |
| Posted | Apr 16, 2019 |
| Download | Microsoft.70-762.SelfTestEngine.2019-04-16.78q.vcex |
How to open VCEX & EXAM Files?
Files with VCEX & EXAM extensions can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Coupon: MASTEREXAM
With discount: 20%





Demo Questions
Question 1

Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You have a database that contains the following tables: BlogCategory, BlogEntry, ProductReview, Product, and SalesPerson. The tables were created using the following Transact SQL statements:

You must modify the ProductReview Table to meet the following requirements:
- The table must reference the ProductID column in the Product table
- Existing records in the ProductReview table must not be validated with the Product table.
- Deleting records in the Product table must not be allowed if records are referenced by the ProductReview table.
- Changes to records in the Product table must propagate to the ProductReview table.
You also have the following databse tables: Order, ProductTypes, and SalesHistory, The transact-SQL statements for these tables are not available.
You must modify the Orders table to meet the following requirements:
- Create new rows in the table without granting INSERT permissions to the table.
- Notify the sales person who places an order whether or not the order was completed.
You must add the following constraints to the SalesHistory table:
- a constraint on the SaleID column that allows the field to be used as a record identifier
- a constant that uses the ProductID column to reference the Product column of the ProductTypes table
- a constraint on the CategoryID column that allows one row with a null value in the column
- a constraint that limits the SalePrice column to values greater than four
Finance department users must be able to retrieve data from the SalesHistory table for sales persons where the value of the SalesYTD column is above a certain threshold.
You plan to create a memory-optimized table named SalesOrder. The table must meet the following requirments:
- The table must hold 10 million unique sales orders.
- The table must use checkpoints to minimize I/O operations and must not use transaction logging.
- Data loss is acceptable.
Performance for queries against the SalesOrder table that use Where clauses with exact equality operations must be optimized.
You need to modify the design of the Orders table.
What should you create?
- a stored procedure with the RETURN statement
- a FOR UPDATE trigger
- an AFTER UPDATE trigger
- a user defined function
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
Requirements: You must modify the Orders table to meet the following requirements:Create new rows in the table without granting INSERT permissions to the table. Notify the sales person who places an order whether or not the order was completed. References:https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms186755.aspx Requirements: You must modify the Orders table to meet the following requirements:
- Create new rows in the table without granting INSERT permissions to the table.
- Notify the sales person who places an order whether or not the order was completed.
References:https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms186755.aspx
Question 2
You have a database that is experiencing deadlock issues when users run queries.
You need to ensure that all deadlocks are recorded in XML format.
What should you do?
- Create a Microsoft SQL Server Integration Services package that uses sys.dm_tran_locks.
- Enable trace flag 1224 by using the Database Cpmsistency Checker(BDCC).
- Enable trace flag 1222 in the startup options for Microsoft SQL Server.
- Use the Microsoft SQL Server Profiler Lock:Deadlock event class.
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
When deadlocks occur, trace flag 1204 and trace flag 1222 return information that is capturedin the SQL Server error log. Trace flag 1204 reports deadlock information formatted by each node involved in the deadlock. Trace flag 1222 formats deadlock information, first by processes and then by resources. The output format for Trace Flag 1222 only returns information in an XML-like format. References:https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms178104(v=sql.105).aspx When deadlocks occur, trace flag 1204 and trace flag 1222 return information that is capturedin the SQL Server error log. Trace flag 1204 reports deadlock information formatted by each node involved in the deadlock. Trace flag 1222 formats deadlock information, first by processes and then by resources.
The output format for Trace Flag 1222 only returns information in an XML-like format.
References:https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms178104(v=sql.105).aspx
Question 3
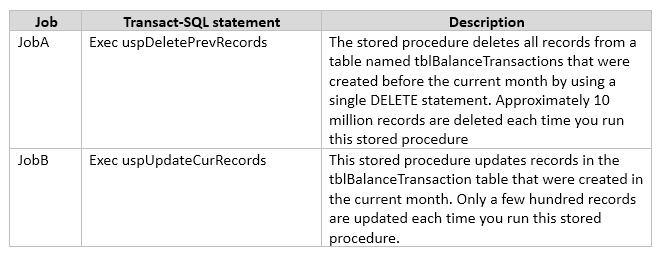
You are developing an application that connects to a database.
The application runs the following jobs:

The READ_COMMITTED_SNAPSHOT database option is set to OFF, and auto-content is set to ON. Within the stored procedures, no explicit transactions are defined.
If JobB starts before JobA, it can finish in seconds. If JobA starts first, JobB takes a long time to complete.
You need to use Microsoft SQL Server Profiler to determine whether the blocking that you observe in JobB is caused by locks acquired by JobA.
Which trace event class in the Locks event category should you use?
- LockAcquired
- LockCancel
- LockDeadlock
- LockEscalation
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
The Lock:Acquiredevent class indicates that acquisition of a lock on a resource, such asa data page, has been achieved.The Lock:Acquired and Lock:Released event classes can be used to monitor when objects are being locked, the type of locks taken, and for how long the locks were retained. Locks retained for long periods of time may cause contention issues and should be investigated. The Lock:Acquiredevent class indicates that acquisition of a lock on a resource, such asa data page, has been achieved.
The Lock:Acquired and Lock:Released event classes can be used to monitor when objects are being locked, the type of locks taken, and for how long the locks were retained. Locks retained for long periods of time may cause contention issues and should be investigated.
Question 4


Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
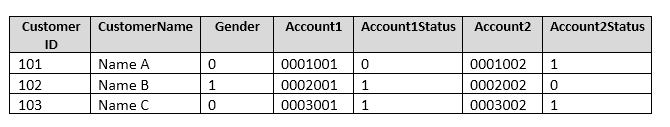
You have a database named DB1 that contains the following tables: Customer, CustomerToAccountBridge, and CustomerDetails. The three tables are part of the Sales schema. The database also contains a schema named Website. You create the Customer table by running the following Transact-SQL statement:

The value of the CustomerStatus column is equal to one for active customers. The value of the Account1Status and Account2Status columns are equal to one for active accounts. The following table displays selected columns and rows from the Customer table.

You plan to create a view named Website.Customer and a view named Sales.FemaleCustomers.
Website.Customer must meet the following requirements:
- Allow users access to the CustomerName and CustomerNumber columns for active customers.
- Allow changes to the columns that the view references. Modified data must be visible through the view.
- Prevent the view from being published as part of Microsoft SQL Server replication.
Sales.Female.Customers must meet the following requirements:
- Allow users access to the CustomerName, Address, City, State and PostalCode columns.
- Prevent changes to the columns that the view references.
- Only allow updates through the views that adhere to the view filter.
You have the following stored procedures: spDeleteCustAcctRelationship and spUpdateCustomerSummary. The spUpdateCustomerSummary stored procedure was created by running the following Transacr-SQL statement:

You run the spUpdateCustomerSummary stored procedure to make changes to customer account summaries. Other stored procedures call the spDeleteCustAcctRelationship to delete records from the CustomerToAccountBridge table.
You must update the design of the Customer table to meet the following requirements.
- You must be able to store up to 50 accounts for each customer.
- Users must be able to retrieve customer information by supplying an account number.
- Users must be able to retrieve an account number by supplying customer information.
You need to implement the design changes while minimizing data redundancy.
What should you do?
- Split the table into three separate tables. Include the AccountNumber and CustomerID columns in the first table. Include the CustomerName and Gender columns in the second table. Include the AccountStatus column in the third table.
- Split the table into two separate tables. Include AccountNumber, CustomerID, CustomerName and Gender columns in the first table. Include the AccountNumber and AccountStatus columns in the second table.
- Split the table into two separate tables, Include the CustomerID and AccountNumber columns in the first table. Include the AccountNumber, AccountStatus, CustomerName and Gender columns in the second table.
- Split the table into two separate tables, Include the CustomerID, CustomerName and Gender columns in the first table. Include AccountNumber, AccountStatus and CustomerID columns in the second table.
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
Two tables is enough.CustomerID must be in both tables. Two tables is enough.CustomerID must be in both tables.
Question 5

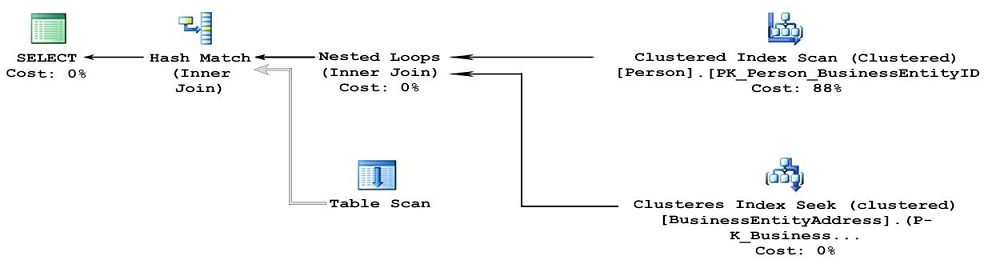
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same or similar answer choices. An answer choice may be correct for more than one question in the series. Each question os independent of the other questions in this series. Information and details provided in a question apply only to that question.
You have a database named DB1. There is no memory-optimized filegroup in the database.
You run the following query:

The following image displays the execution plan the query optimizer generates for this query:

Users frequently run the same query with different values for the local variable @lastName. The table named Person is persisted on disk.
You need to create an index on the Person.Person table that meets the following requirements:
- All users must be able to benefit from the index.
- FirstName must be added to the index as an included column.
What should you do?
- Create a clustered index on the table.
- Create a nonclustered index on the table.
- Create a nonclustered filtered index on the table.
- Create a clustered columnstore index on the table.
- Create a nonclustered columnstore index on the table.
- Create a hash index on the table.
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
By including nonkey columns, you can create nonclustered indexes that cover more queries. This is because the nonkeycolumns have the following benefits:They can be data types not allowed as index key columns. They are not considered by the Database Engine when calculating the number of index key columns or index key size. By including nonkey columns, you can create nonclustered indexes that cover more queries. This is because the nonkeycolumns have the following benefits:
They can be data types not allowed as index key columns.
They are not considered by the Database Engine when calculating the number of index key columns or index key size.
Question 6
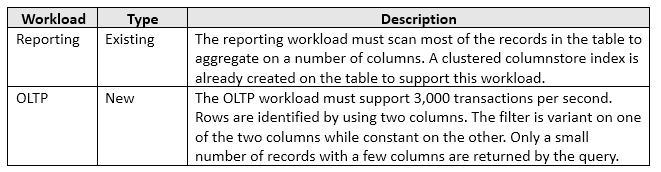
Note: The question is part of a series of questions that use the same or similar answer choices. An answer choice may be correct for more than one question in the series. Each question is independent of the other question in the series. Information and details provided in a question apply only to that question.
You have a database named DB1. The database does not use a memory-optimized filegroup. The database contains a table named Table1. The table must support the following workloads:

You need to add the most efficient index to support the new OLTP workload, while not deteriorating the existing Reporting query performance.
What should you do?
- Create a clustered index on the table.
- Create a nonclustered index on the table.
- Create a nonclustered filtered index on the table.
- Create a clustered columnstore index on the table.
- Create a nonclustered columnstore index on the table.
- Create a hash index on the table.
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
A filtered index is an optimized nonclustered index, especially suited to cover queries that select from a well-defined subset of data. It uses a filter predicate to index a portion of rows in the table. A well-designed filtered index can improve query performance, reduce index maintenance costs, and reduce index storage costs compared with full-table indexes. References:https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc280372(v=sql.105).aspx A filtered index is an optimized nonclustered index, especially suited to cover queries that select from a well-defined subset of data. It uses a filter predicate to index a portion of rows in the table. A well-designed filtered index can improve query performance, reduce index maintenance costs, and reduce index storage costs compared with full-table indexes.
References:https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc280372(v=sql.105).aspx
Question 7

Note: The question is part of a series of questions that use the same or similar answer choices. An answer choice may be correct for more than one question in the series. Each question is independent of the other question in the series. Information and details provided in a question apply only to that question.
You have a database named DB1. The database does not have a memory optimized filegroup.
You create a table by running the following Transact-SQL statement:

The table is currently used for OLTP workloads. The analytics user group needs to perform real-time operational analytics that scan most of the records in the table to aggregate on a number of columns.
You need to add the most efficient index to support the analytics workload without changing the OLTP application.
What should you do?
- Create a clustered indexon the table.
- Create a nonclustered index on the table.
- Create a nonclustered filtered index on the table.
- Create a clustered columnstore index on the table.
- Create a nonclustered columnstore index on the table.
- Create a hash index on the table.
Correct answer: E
Explanation:
A nonclustered columnstore index enables real-time operational analytics in which the OLTP workload uses the underlying clustered index, while analytics run concurrently on the columnstore index. Columnstore indexes can achieve up to 100xbetter performance on analytics and data warehousing workloads and up to 10x better data compression than traditional rowstore indexes. These recommendations will help your queries achieve the very fast query performance that columnstore indexes are designed to provide. References:https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/gg492088.aspx A nonclustered columnstore index enables real-time operational analytics in which the OLTP workload uses the underlying clustered index, while analytics run concurrently on the columnstore index.
Columnstore indexes can achieve up to 100xbetter performance on analytics and data warehousing workloads and up to 10x better data compression than traditional rowstore indexes. These recommendations will help your queries achieve the very fast query performance that columnstore indexes are designed to provide.
References:https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/gg492088.aspx
Question 8
You use Microsoft SQL Server Profile to evaluate a query named Query1. The Profiler report indicates the following issues:
- At each level of the query plan, a low total number of rows are processed.
- The query uses many operations. This results in a high overall cost for the query.
You need to identify the information that will be useful for the optimizer.
What should you do?
- Start a SQL Server Profiler trace for the event class Auto Stats in the Performance event category.
- Create one Extended Events session with the sqlserver.missing_column_statistics event added.
- Start a SQL Server Profiler trace for the event class Soft Warnings in the Errors and Warnings event category.
- Create one Extended Events session with the sqlserver.missing_join_predicate event added.
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
The Missing Join Predicate event class indicates that a query is being executed that has no join predicate. This could result in a long-running query. The Missing Join Predicate event class indicates that a query is being executed that has no join predicate. This could result in a long-running query.
Question 9
You are experiencing performance issues with the database server.
You need to evaluate schema locking issues, plan cache memory pressure points, and backup I/O problems.
What should you create?
- a System Monitor report
- a sys.dm_exec_query_stats dynamic management view query
- a sys.dm_exec_session_wait_stats dynamicmanagement view query
- an Activity Monitor session in Microsoft SQL Management Studio.
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
sys.dm_exec_session_wait_stats returns information about all the waits encountered by threads that executed for each session. You can use this view to diagnose performance issues with the SQL Server session and also with specific queries and batches. Note: SQL Server wait stats are, at their highest conceptual level, grouped into two broad categories: signal waits and resource waits. A signal wait is accumulated by processes running on SQL Server which are waiting for a CPU to become available (so called because the process has “signaled” that it is ready for processing). A resource wait is accumulated by processes running on SQL Server which are waiting fora specific resource to become available, such as waiting for the release of a lock on a specific record. sys.dm_exec_session_wait_stats returns information about all the waits encountered by threads that executed for each session. You can use this view to diagnose performance issues with the SQL Server session and also with specific queries and batches.
Note: SQL Server wait stats are, at their highest conceptual level, grouped into two broad categories: signal waits and resource waits. A signal wait is accumulated by processes running on SQL Server which are waiting for a CPU to become available (so called because the process has “signaled” that it is ready for processing). A resource wait is accumulated by processes running on SQL Server which are waiting fora specific resource to become available, such as waiting for the release of a lock on a specific record.
Question 10
Note: this question is part of a series of questions that use the same or similar answer choices. An answer choice may be correct for more than one question in the series. Each question is independent of the other questions in the series. Information and details provided in a question apply only to that question.
You are developing an application to track customer sales.
You need to create a database object that meets the following requirements:
- Return a value of 0 if data inserted successfully into the Customers table.
- Return a value of 1 if data is not inserted successfully into the Customers table.
- Support logic that is written by using managed code.
What should you create?
- extended procedure
- CLR procedure
- user-defined procedure
- DML trigger
- DDL trigger
- scalar-valued function
- table-valued function
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
DML triggers is a special type of stored procedure that automatically takes effect when a data manipulation language (DML) event takes place that affects the table or view defined in the trigger. DML events include INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statements.DML triggers can be used to enforce business rules and data integrity, query other tables, and include complex Transact-SQL statements. A CLR trigger is a type of DDL trigger. A CLR Trigger can be either an AFTER or INSTEAD OF trigger. A CLR trigger canalso be a DDL trigger. Instead of executing a Transact-SQL stored procedure, a CLR trigger executes one or more methods written in managed code that are members of an assembly created in the .NET Framework and uploaded in SQL Server. References:https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms178110.aspx DML triggers is a special type of stored procedure that automatically takes effect when a data manipulation language (DML) event takes place that affects the table or view defined in the trigger. DML events include INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statements.DML triggers can be used to enforce business rules and data integrity, query other tables, and include complex Transact-SQL statements.
A CLR trigger is a type of DDL trigger. A CLR Trigger can be either an AFTER or INSTEAD OF trigger. A CLR trigger canalso be a DDL trigger. Instead of executing a Transact-SQL stored procedure, a CLR trigger executes one or more methods written in managed code that are members of an assembly created in the .NET Framework and uploaded in SQL Server.
References:https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms178110.aspx

