File Info
| Exam | Developing SQL Databases |
| Number | 70-762 |
| File Name | Microsoft.70-762.Test4Prep.2018-07-12.68q.tqb |
| Size | 4 MB |
| Posted | Jul 12, 2018 |
| Download | Microsoft.70-762.Test4Prep.2018-07-12.68q.tqb |
How to open VCEX & EXAM Files?
Files with VCEX & EXAM extensions can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Coupon: MASTEREXAM
With discount: 20%





Demo Questions
Question 1
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
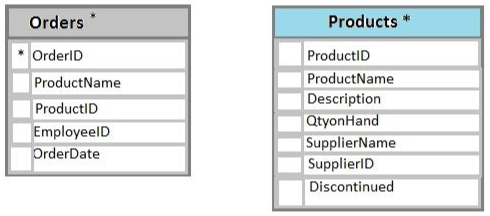
You have a database named Sales that contains the following database tables: Customer, Order, and Products. The Products table and the Order table are shown in the following diagram.

The customer table includes a column that stores the data for the last order that the customer placed.
You plan to create a table named Leads. The Leads table is expected to contain approximately 20,000 records. Storage requirements for the Leads table must be minimized.
Changes to the price of any product must be less a 25 percent increase from the current price. The shipping department must be notified about order and shipping details when an order is entered into the database.
You need to implement the appropriate table objects.
Which object should you use for each table? To answer, drag the appropriate objects to the correct tables. Each object may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
Correct answer: To work with this question, an Exam Simulator is required.
Explanation:
The Products table needs a primary key constraint on the ProductID field. The Orders table needs a foreign key constraint on the productID field, with a reference to the ProductID field in the Products table. The Products table needs a primary key constraint on the ProductID field.
The Orders table needs a foreign key constraint on the productID field, with a reference to the ProductID field in the Products table.
Question 2
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
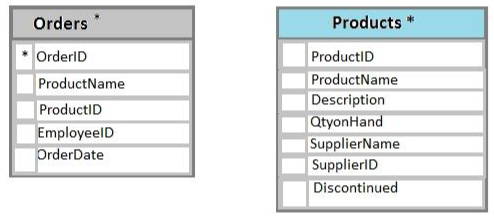
You have a database named Sales that contains the following database tables: Customer, Order, and Products. The Products table and the Order table are shown in the following diagram.

The customer table includes a column that stores the data for the last order that the customer placed.
You plan to create a table named Leads. The Leads table is expected to contain approximately 20,000 records. Storage requirements for the Leads table must be minimized.
You need to implement a stored procedure that deletes a discontinued product from the Products table. You identify the following requirements:
- If an open order includes a discontinued product, the records for the product must not be deleted.
- The stored procedure must return a custom error message if a product record cannot be deleted. The message must identify the OrderID for the open order.
What should you do? To answer, select the appropriate Transact-SQL segments in the answer area.
Correct answer: To work with this question, an Exam Simulator is required.
Explanation:
Using TRY...CATCH in Transact-SQL Errors in Transact-SQL code can be processed by using a TRY…CATCH construct. TRY…CATCH can use the following error function to capture error information:ERROR_MESSAGE() returns the complete text of the error message. The text includes the values supplied for any substitutable parameters such as lengths, object names, or times. References:https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms179296(v=sql.105).aspx Using TRY...CATCH in Transact-SQL
Errors in Transact-SQL code can be processed by using a TRY…CATCH construct.
TRY…CATCH can use the following error function to capture error information:
ERROR_MESSAGE() returns the complete text of the error message. The text includes the values supplied for any substitutable parameters such as lengths, object names, or times.
References:https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms179296(v=sql.105).aspx
Question 3

Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You have a database that contains the following tables: BlogCategory, BlogEntry, ProductReview, Product, and SalesPerson. The tables were created using the following Transact SQL statements:

You must modify the ProductReview Table to meet the following requirements:
- The table must reference the ProductID column in the Product table
- Existing records in the ProductReview table must not be validated with the Product table.
- Deleting records in the Product table must not be allowed if records are referenced by the ProductReview table.
- Changes to records in the Product table must propagate to the ProductReview table.
You also have the following databse tables: Order, ProductTypes, and SalesHistory, The transact-SQL statements for these tables are not available.
You must modify the Orders table to meet the following requirements:
- Create new rows in the table without granting INSERT permissions to the table.
- Notify the sales person who places an order whether or not the order was completed.
You must add the following constraints to the SalesHistory table:
- a constraint on the SaleID column that allows the field to be used as a record identifier
- a constant that uses the ProductID column to reference the Product column of the ProductTypes table
- a constraint on the CategoryID column that allows one row with a null value in the column
- a constraint that limits the SalePrice column to values greater than four
Finance department users must be able to retrieve data from the SalesHistory table for sales persons where the value of the SalesYTD column is above a certain threshold.
You plan to create a memory-optimized table named SalesOrder. The table must meet the following requirments:
- The table must hold 10 million unique sales orders.
- The table must use checkpoints to minimize I/O operations and must not use transaction logging.
- Data loss is acceptable.
Performance for queries against the SalesOrder table that use Where clauses with exact equality operations must be optimized.
You need to enable referential integrity for the ProductReview table.
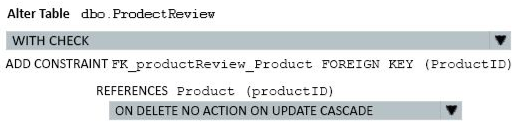
How should you complete the relevant Transact-SQL statement? To answer? select the appropriate Transact-SQL segments in the answer area.

Select two alternatives.
- For the first selection select: WITH CHECK
- For the first selection select: WITH NOCHECK
- For the second selection select: ON DELETE NO ACTION ON UPDATE CASCADE
- For the secondselection select: ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE
- For the second selection select: ON DELETE NO ACTION ON UPDATE NO ACTION
- For the second selection select: ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE NO ACTION
Correct answer: BC
Explanation:
B: We should use WITH NOCHECK asexisting records in the ProductReview table must not be validated with the Product table.C: Deletes should not be allowed, so we use ON DELETE NO ACTION.Updates should be allowed, so we use ON DELETE NO CASCADE NO ACTION: the Database Engine raises an error,and the update action on the row in the parent table is rolled back.CASCADE: corresponding rows are updated in the referencing table when that row is updated in the parent table.Note: ON DELETE { NO ACTION | CASCADE | SET NULL | SET DEFAULT }Specifieswhat action happens to rows in the table that is altered, if those rows have a referential relationship and the referenced row is deleted from the parent table. The default is NO ACTION. ON UPDATE { NO ACTION | CASCADE | SET NULL | SET DEFAULT } Specifieswhat action happens to rows in the table altered when those rows have a referential relationship and the referenced row is updated in the parent table. The default is NO ACTION. Note: You must modify the ProductReview Table to meet the following requirements:The table must reference the ProductID column in the Product table Existing records in the ProductReview table must not be validated with the Product table. Deleting records in the Product table must not be allowed if records are referencedby the ProductReview table. Changes to records in the Product table must propagate to the ProductReview table. References:https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms190273.aspxhttps://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms188066.aspx B: We should use WITH NOCHECK asexisting records in the ProductReview table must not be validated with the Product table.
C: Deletes should not be allowed, so we use ON DELETE NO ACTION.
Updates should be allowed, so we use ON DELETE NO CASCADE
NO ACTION: the Database Engine raises an error,and the update action on the row in the parent table is rolled back.
CASCADE: corresponding rows are updated in the referencing table when that row is updated in the parent table.
Note: ON DELETE { NO ACTION | CASCADE | SET NULL | SET DEFAULT }
Specifieswhat action happens to rows in the table that is altered, if those rows have a referential relationship and the referenced row is deleted from the parent table. The default is NO ACTION.
ON UPDATE { NO ACTION | CASCADE | SET NULL | SET DEFAULT }
Specifieswhat action happens to rows in the table altered when those rows have a referential relationship and the referenced row is updated in the parent table. The default is NO ACTION.
Note: You must modify the ProductReview Table to meet the following requirements:
- The table must reference the ProductID column in the Product table
- Existing records in the ProductReview table must not be validated with the Product table.
- Deleting records in the Product table must not be allowed if records are referencedby the ProductReview table.
- Changes to records in the Product table must propagate to the ProductReview table.
References:https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms190273.aspx
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms188066.aspx

