File Info
| Exam | Networking Fundamentals |
| Number | 98-366 |
| File Name | Microsoft.98-366.PracticeTest.2018-09-06.88q.vcex |
| Size | 514 KB |
| Posted | Sep 06, 2018 |
| Download | Microsoft.98-366.PracticeTest.2018-09-06.88q.vcex |
How to open VCEX & EXAM Files?
Files with VCEX & EXAM extensions can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Coupon: MASTEREXAM
With discount: 20%





Demo Questions
Question 1
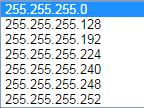
Which subnet mask is valid?
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.228
- 255.255.255.164
- 255.255.255.245
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
These are valid: These are valid:

Question 2
A service that resolves NetBIOS names to IP addresses is:
- Domain Name Service (DNS).
- Internet Service Provider (ISP).
- Address Resolution Protocol (ARP).
- Windows Internet Name Service (WINS).
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
Windows Internet Name Service (WINS) is Microsoft's implementation of NetBIOS Name Service (NBNS), a name server and service for NetBIOS computer names. Effectively, WINS is to NetBIOS names what DNS is to domain names — a central mapping of host names to network addresses. Windows Internet Name Service (WINS) is Microsoft's implementation of NetBIOS Name Service (NBNS), a name server and service for NetBIOS computer names. Effectively, WINS is to NetBIOS names what DNS is to domain names — a central mapping of host names to network addresses.
Question 3
What type of DNS record maps host names to addresses?
- Mail Exchanger (MX) DNS record
- Service (SRV) DNS record
- Host (A) DNS record
- Canonical (CNAME) DNS record
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
An A or Address record (also known as a host record) links a domain to the physical IP address of a computer hosting that domain's services. An A or Address record (also known as a host record) links a domain to the physical IP address of a computer hosting that domain's services.
Question 4
Teredo tunneling is a protocol that:
- Translates Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) to Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6).
- Allows IPv6 connectivity through IPv4 devices.
- Provides VPN security.
- Dynamically allocates IPv6 addresses.
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
Teredo alleviates this problem by encapsulating IPv6 packets within UDP/IPv4 datagrams, which most NATs can forward properly. Thus, IPv6-aware hosts behind NATs can be used as Teredo tunnel endpoints even when they don't have a dedicated public IPv4 address. Teredo alleviates this problem by encapsulating IPv6 packets within UDP/IPv4 datagrams, which most NATs can forward properly. Thus, IPv6-aware hosts behind NATs can be used as Teredo tunnel endpoints even when they don't have a dedicated public IPv4 address.
Question 5
What is the default subnet mask for a Class C Internet network?
- 255.255.255.252
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.0
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
Class A default subnet mask is 255.0.0.0. Class B default subnet mask is 255.255.0.0. Class C default subnet mask is 255.255.255.0. Class A default subnet mask is 255.0.0.0.
Class B default subnet mask is 255.255.0.0.
Class C default subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.
Question 6
The default port used for telnet is:
- 23
- 25
- 80
- 8080
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
The telnet protocol is used to establish a connection to Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) port number 23, where a Telnet server application (telnetd) is listening. The telnet protocol is used to establish a connection to Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) port number 23, where a Telnet server application (telnetd) is listening.
Question 7
When a client's DHCP-issued address expires, the client will:
- Select a new address and request approval from the DHCP server.
- Require manual configuration with a static IP address.
- Attempt to obtain a new address by broadcasting.
- Continue to use the address until it is notified to stop.
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
Rebinding would occur. Rebinding If the DHCP client is unable to communicate with the DHCP server from which it obtained its lease, and 87.5 percent of its lease time has expired, it will attempt to contact any available DHCP server by broadcasting DHCPRequest messages. Any DHCP server can respond with a DHCPAck message, renewing the lease, or a DHCPNak message, forcing the DHCP client to initialize and restart the lease process. Note: Renewing IP addressing information is leased to a client, and the client is responsible for renewing the lease. By default, DHCP clients try to renew their lease when 50 percent of the lease time has expired. To renew its lease, a DHCP client sends a DHCPRequest message to the DHCP server from which it originally obtained the lease. Reference: DHCP Client States in the Lease Process Rebinding would occur.
Rebinding
If the DHCP client is unable to communicate with the DHCP server from which it obtained its lease, and 87.5 percent of its lease time has expired, it will attempt to contact any available DHCP server by broadcasting DHCPRequest messages. Any DHCP server can respond with a DHCPAck message, renewing the lease, or a DHCPNak message, forcing the DHCP client to initialize and restart the lease process.
Note:
Renewing
IP addressing information is leased to a client, and the client is responsible for renewing the lease. By default, DHCP clients try to renew their lease when 50 percent of the lease time has expired. To renew its lease, a DHCP client sends a DHCPRequest message to the DHCP server from which it originally obtained the lease.
Reference: DHCP Client States in the Lease Process
Question 8
You ping a server by using fully qualified domain name (FQDN) and do not receive a response. You then ping the same server by using its IP address and receive a response.
Why do you receive a response on the second attempt but not on the first attempt?
- PING is improperly configured.
- The DNS is not resolving.
- The DHCP server is offline.
- NSLOOKUP is stopped.
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
DNS is not working. DNS is not working.
Question 9
A Media Access Control (MAC) address identifies a/an:
- UPnP device.
- Local broadcast domain.
- Network interface card (NIC).
- Local area network (LAN).
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
A media access control address (MAC address) is a unique identifier assigned to network interfaces for communications on the physical network segment. A media access control address (MAC address) is a unique identifier assigned to network interfaces for communications on the physical network segment.
Question 10
Two companies want to share data by using the Internet.
Which type of network provides the solution?
- Ethernet
- Intranet
- Extranet
- Perimeter
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
An extranet is a computer network that allows controlled access from outside of an organization's intranet. Extranets are used for specific use cases including business-to-business (B2B). An extranet is a computer network that allows controlled access from outside of an organization's intranet. Extranets are used for specific use cases including business-to-business (B2B).

