File Info
| Exam | Oracle Datbase 12c SQL |
| Number | 1z0-071 |
| File Name | Oracle.1z0-071.ActualTests.2018-09-24.100q.vcex |
| Size | 7 MB |
| Posted | Sep 24, 2018 |
| Download | Oracle.1z0-071.ActualTests.2018-09-24.100q.vcex |
How to open VCEX & EXAM Files?
Files with VCEX & EXAM extensions can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Coupon: MASTEREXAM
With discount: 20%





Demo Questions
Question 1
Which two statements are true regarding the EXISTS operator used in the correlated subqueries? (Choose two.)
- The outer query stops evaluating the result set of the inner query when the first value is found.
- It is used to test whether the values retrieved by the inner query exist in the result of the outer query.
- It is used to test whether the values retrieved by the outer query exist in the result set of the inner query.
- The outer query continues evaluating the result set of the inner query until all the values in the result set are processed.
Correct answer: AC
Explanation:
References:http://www.techonthenet.com/oracle/exists.php References:
http://www.techonthenet.com/oracle/exists.php
Question 2

View the exhibit and examine the structure of the STORES table.

You want to display the NAME of the store along with the ADDRESS, START_DATE, PROPERTY_PRICE, and the projected property price, which is 115% of property price.
The stores displayed must have START_DATE in the range of 36 months starting from 01-Jan-2000 and above.
Which SQL statement would get the desired output?
- SELECT name, concat (address| | ','| |city| |', ', country) AS full_address,start_date,property_price, property_price*115/100FROM storesWHERE MONTHS_BETWEEN (start_date, '01-JAN-2000') <=36;
- SELECT name, concat (address| | ','| |city| |', ', country) AS full_address,start_date,property_price, property_price*115/100FROM storesWHERE TO_NUMBER(start_date-TO_DATE('01-JAN-2000','DD-MON-RRRR')) <=36;
- SELECT name, address||','||city||','||country AS full_address,start_date,property_price, property_price*115/100FROM storesWHERE MONTHS_BETWEEN (start_date, TO_DATE('01-JAN-2000','DD-MON-RRRR')) <=36;
- SELECT name, concat (address||','| |city| |', ', country) AS full_address,start_date,property_price, property_price*115/100FROM storesWHERE MONTHS_BETWEEN (start_date, TO_DATE('01-JAN-2000','DD-MON-RRRR')) <=36;
Correct answer: D
Question 3
The BOOKS_TRANSACTIONS table exists in your database.
SQL>SELECT * FROM books_transactions ORDER BY 3;
What is the outcome on execution?
- The execution fails unless the numeral 3 in the ORDER BY clause is replaced by a column name.
- Rows are displayed in the order that they are stored in the table only for the three rows with the lowest values in the key column.
- Rows are displayed in the order that they are stored in the table only for the first three rows.
- Rows are displayed sorted in ascending order of the values in the third column in the table.
Correct answer: D
Question 4

Examine the command:

What does ON DELETE CASCADE imply?
- When the BOOKS table is dropped, the BOOK_TRANSACTIONS table is dropped.
- When the BOOKS table is dropped, all the rows in the BOOK_TRANSACTIONS table are deleted but the table structure is retained.
- When a row in the BOOKS table is deleted, the rows in the BOOK_TRANSACTIONS table whose BOOK_ID matches that of the deleted row in the BOOKS table are also deleted.
- When a value in the BOOKS.BOOK_ID column is deleted, the corresponding value is updated in the BOOKS_TRANSACTIONS.BOOK_ID column.
Correct answer: C
Question 5
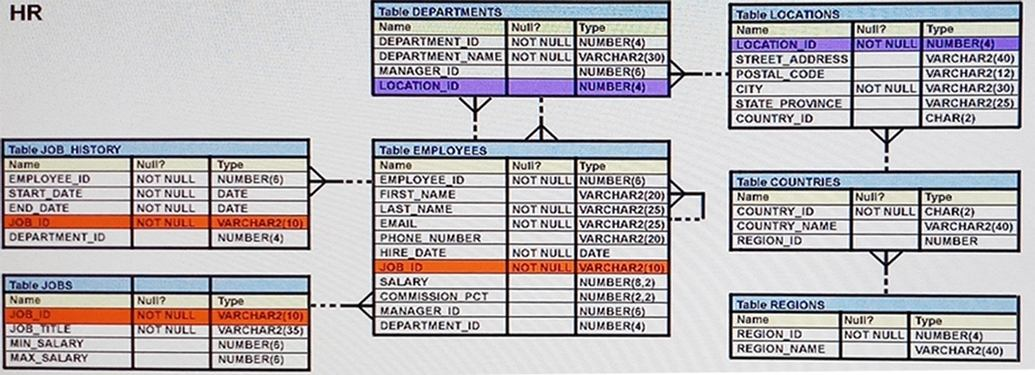
View the exhibit and examine the structure of the EMPLOYEES table.

You want to display all employees and their managers having 100 as the MANAGER_ID. You want the output in two columns: the first column would have the LAST_NAME of the managers and the second column would have LAST_NAME of the employees.
Which SQL statement would you execute?
- SELECT m.last_name "Manager", e.last_name "Employee"FROM employees m JOIN employees eON m.employee_id = e.manager_idWHERE m.manager_id = 100;
- SELECT m.last_name "Manager", e.last_name "Employee"FROM employees m JOIN employees eON m.employee_id = e.manager_idWHERE e.manager_id = 100;
- SELECT m.last_name "Manager", e.last_name "Employee"FROM employees m JOIN employees eON e.employee_id = m.manager_idWHERE m.manager_id = 100;
- SELECT m.last_name "Manager", e.last_name "Employee"FROM employees m JOIN employees eWHERE m.employee_id = e.manager_id and AND e.manager_id = 100
Correct answer: B
Question 6
Which three statements are true about multiple-row subqueries?
- They can contain a subquery within a subquery.
- They can return multiple columns as well as rows.
- They cannot contain a subquery within a subquery.
- They can return only one column but multiple rows.
- They can contain group functions and GROUP BY and HAVING clauses.
- They can contain group functions and the GROUP BY clause, but not the HAVING clause.
Correct answer: ABE
Question 7
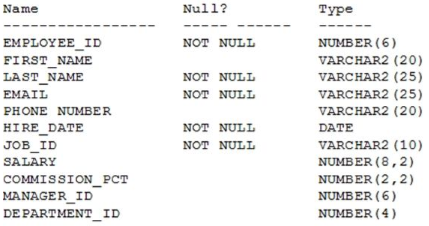
Examine the structure of the EMPLOYEES table.

There is a parent/child relationship between EMPLOYEE_ID and MANAGER_ID.
You want to display the last names and manager IDs of employees who work for the same manager as the employee whose EMPLOYEE_ID is 123.
Which query provides the correct output?
- SELECT e.last_name, m.manager_idFROM employees e RIGHT OUTER JOIN employees mon (e.manager_id = m.employee_id)AND e.employee_id = 123;
- SELECT e.last_name, m.manager_idFROM employees e LEFT OUTER JOIN employees mon (e.employee_id = m.manager_id)WHERE e.employee_id = 123;
- SELECT e.last_name, e.manager_idFROM employees e RIGHT OUTER JOIN employees mon (e.employee_id = m.employee_id)WHERE e.employee_id = 123;
- SELECT m.last_name, e.manager_idFROM employees e LEFT OUTER JOIN employees mon (e.manager_id = m.manager_id)WHERE e.employee_id = 123;
Correct answer: D
Question 8
Which normal form is a table in if it has no multi-valued attributes and no partial dependencies?
- second normal form
- first normal form
- third normal form
- fourth normal form
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
References:https://blog.udemy.com/database-normal-forms/ References:
https://blog.udemy.com/database-normal-forms/
Question 9
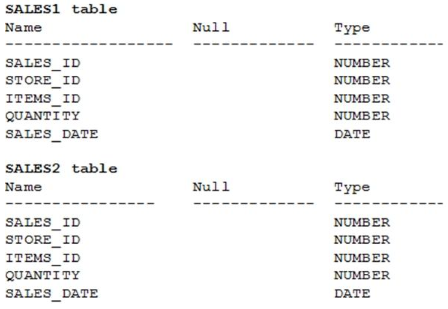
Sales data of a company is stored in two tables, SALES1 and SALES2, with some data being duplicated across the tables. You want to display the results from the SALES1 table, which are not present in the SALES2 table.

Which set operator generates the required output?
- INTERSECT
- UNION
- PLUS
- MINUS
- SUBTRACT
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
References:https://docs.oracle.com/cd/B19306_01/server.102/b14200/queries004.htm References:
https://docs.oracle.com/cd/B19306_01/server.102/b14200/queries004.htm
Question 10
Evaluate the following ALTER TABLE statement:
ALTER TABLE orders
SET UNUSED (order_date);
Which statement is true?
- After executing the ALTER TABLE command, you can add a new column called ORDER_DATE to the ORDERS table.
- The ORDER_DATE column should be empty for the ALTER TABLE command to execute successfully.
- ROLLBACK can be used to get back the ORDER_DATE column in the ORDERS table.
- The DESCRIBE command would still display the ORDER_DATE column.
Correct answer: A

