File Info
| Exam | SnowPro Core Recertification |
| Number | COF-R02 |
| File Name | Snowflake.COF-R02.VCEplus.2024-10-21.142q.vcex |
| Size | 610 KB |
| Posted | Oct 21, 2024 |
| Download | Snowflake.COF-R02.VCEplus.2024-10-21.142q.vcex |
How to open VCEX & EXAM Files?
Files with VCEX & EXAM extensions can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Coupon: MASTEREXAM
With discount: 20%





Demo Questions
Question 1
A user has unloaded data from Snowflake to a stage
Which SQL command should be used to validate which data was loaded into the stage?
- list @file__stage
- show @file__stage
- view @file__stage
- verify @file__stage
Correct answer: A
Question 2
What happens when a cloned table is replicated to a secondary database? (Select TWO)
- A read-only copy of the cloned tables is stored.
- The replication will not be successful.
- The physical data is replicated
- Additional costs for storage are charged to a secondary account
- Metadata pointers to cloned tables are replicated
Correct answer: CD
Explanation:
Cloned objects are replicated physically rather than logically to secondary databases. That is, cloned tables in a standard database do not contribute to the overall data storage unless or until DML operations on the clone add to or modify existing data. However, when a cloned table is replicated to a secondary database, the physical data is also replicated, increasing the data storage usage for your account.https://docs.snowflake.com/en/user-guide/database-replicationconsiderations.html#:~:text=Replication%20and%20Cloning,-Cloned%20objects%20are&text=However%2C%20when%20a%20cloned%20table,storage%20usage%20for%20your%20account. Cloned objects are replicated physically rather than logically to secondary databases. That is, cloned tables in a standard database do not contribute to the overall data storage unless or until DML operations on the clone add to or modify existing data. However, when a cloned table is replicated to a secondary database, the physical data is also replicated, increasing the data storage usage for your account.
https://docs.snowflake.com/en/user-guide/database-replicationconsiderations.html#:~:text=Replication%20and%20Cloning,-
Cloned%20objects%20are&text=However%2C%20when%20a%20cloned%20table,storage%20usage%20for%20your%20account.
Question 3
Which command should be used to download files from a Snowflake stage to a local folder on a client's machine?
- PUT
- GET
- COPY
- SELECT
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.snowflake.com/en/sql-reference/sql/get.html Reference: https://docs.snowflake.com/en/sql-reference/sql/get.html
Question 4
How does Snowflake Fail-safe protect data in a permanent table?
- Fail-safe makes data available up to 1 day, recoverable by user operations.
- Fail-safe makes data available for 7 days, recoverable by user operations.
- Fail-safe makes data available for 7 days, recoverable only by Snowflake Support.
- Fail-safe makes data available up to 1 day, recoverable only by Snowflake Support.
Correct answer: C
Question 5
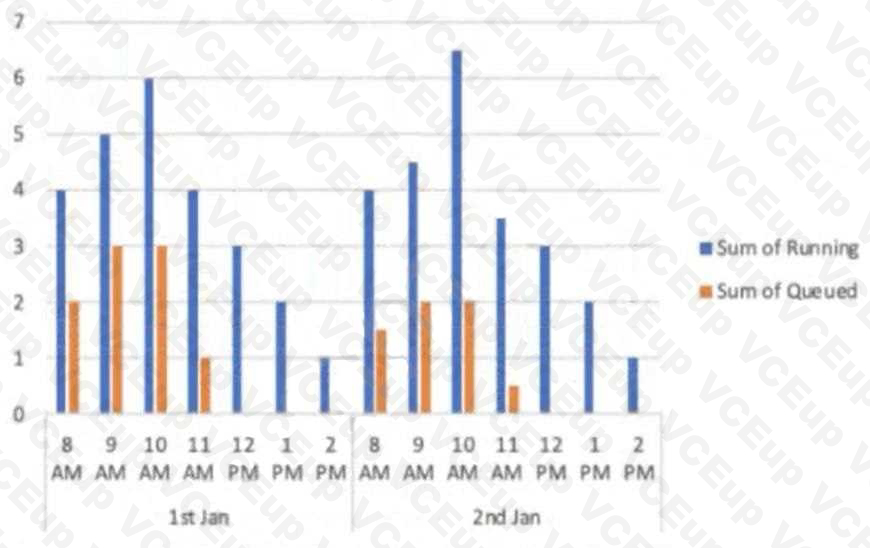
A virtual warehouse is created using the following command:
Create warehouse my_WH with
warehouse_size = MEDIUM
min_cluster_count = 1
max_cluster_count = 1
auto_suspend = 60
auto_resume = true;
The image below is a graphical representation of the warehouse utilization across two days.

What action should be taken to address this situation?
- Increase the warehouse size from Medium to 2XL.
- Increase the value for the parameter MAX_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL.
- Configure the warehouse to a multi-cluster warehouse.
- Lower the value of the parameter STATEMENT_QUEUED_TIMEOUT_IN_SECONDS.
Correct answer: B
Question 6
Which minimum Snowflake edition allows for a dedicated metadata store?
- Standard
- Enterprise
- Business Critical
- Virtual Private Snowflake
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.snowflake.com/en/user-guide/intro-editions.html Reference: https://docs.snowflake.com/en/user-guide/intro-editions.html
Question 7
Network policies can be set at which Snowflake levels? (Choose two.)
- Role
- Schema
- User
- Database
- Account
- Tables
Correct answer: CE
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.snowflake.com/en/user-guide/network-policies.html#creating-networkpolicies Reference: https://docs.snowflake.com/en/user-guide/network-policies.html#creating-networkpolicies
Question 8
What are the correct parameters for time travel and fail-safe in the Snowflake Enterprise Edition?
- Default Time Travel Retention is set to 0 days.Maximum Time Travel Retention is 30 days.Fail Safe retention time is 1 day.
- Default Time Travel Retention is set to 1 day.Maximum Time Travel Retention is 365 days.Fail Safe retention time is 7 days.
- Default Time Travel Retention is set to 0 days.Maximum Time Travel Retention is 90 days.Fail Safe retention time is 7 days.
- Default Time Travel Retention is set to 1 day.Maximum Time Travel Retention is 90 days.Fail Safe retention time is 7 days.
- Default Time Travel Retention is set to 7 days.Maximum Time Travel Retention is 1 day.Fail Safe retention time is 90 days.
- Default Time Travel Retention is set to 90 days.Maximum Time Travel Retention is 7 days.Fail Safe retention time is 356 days.
Correct answer: D
Question 9
Which data types does Snowflake support when querying semi-structured data? (Select TWO)
- VARIANT
- ARRAY
- VARCHAR
- XML
- BLOB
Correct answer: AB
Explanation:
https://docs.snowflake.com/en/user-guide/semistructured-intro.html#label-loading-semi-structured-dataA VARIANT stores semi-structured data in Snowflake. It can store a value of any other type, including OBJECT and ARRAY.The maximum length of a VARIANT is 16 MB.A Snowflake ARRAY is similar to an array in many other programming languages. An ARRAY contains 0 or more pieces of data. Each element is accessed by specifying its position in the array. https://docs.snowflake.com/en/user-guide/semistructured-intro.html#label-loading-semi-structured-data
A VARIANT stores semi-structured data in Snowflake. It can store a value of any other type, including OBJECT and ARRAY.
The maximum length of a VARIANT is 16 MB.
A Snowflake ARRAY is similar to an array in many other programming languages. An ARRAY contains 0 or more pieces of data. Each element is accessed by specifying its position in the array.
Question 10
Which of the following describes how multiple Snowflake accounts in a single organization relate to various cloud providers?
- Each Snowflake account can be hosted in a different cloud vendor and region.
- Each Snowflake account must be hosted in a different cloud vendor and region
- All Snowflake accounts must be hosted in the same cloud vendor and region
- Each Snowflake account can be hosted in a different cloud vendor, but must be in the same region.
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
https://docs.snowflake.com/en/user-guide/intro-regions.html https://docs.snowflake.com/en/user-guide/intro-regions.html


